- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Platelet-rich plasma shows efficacy in melasma- a review
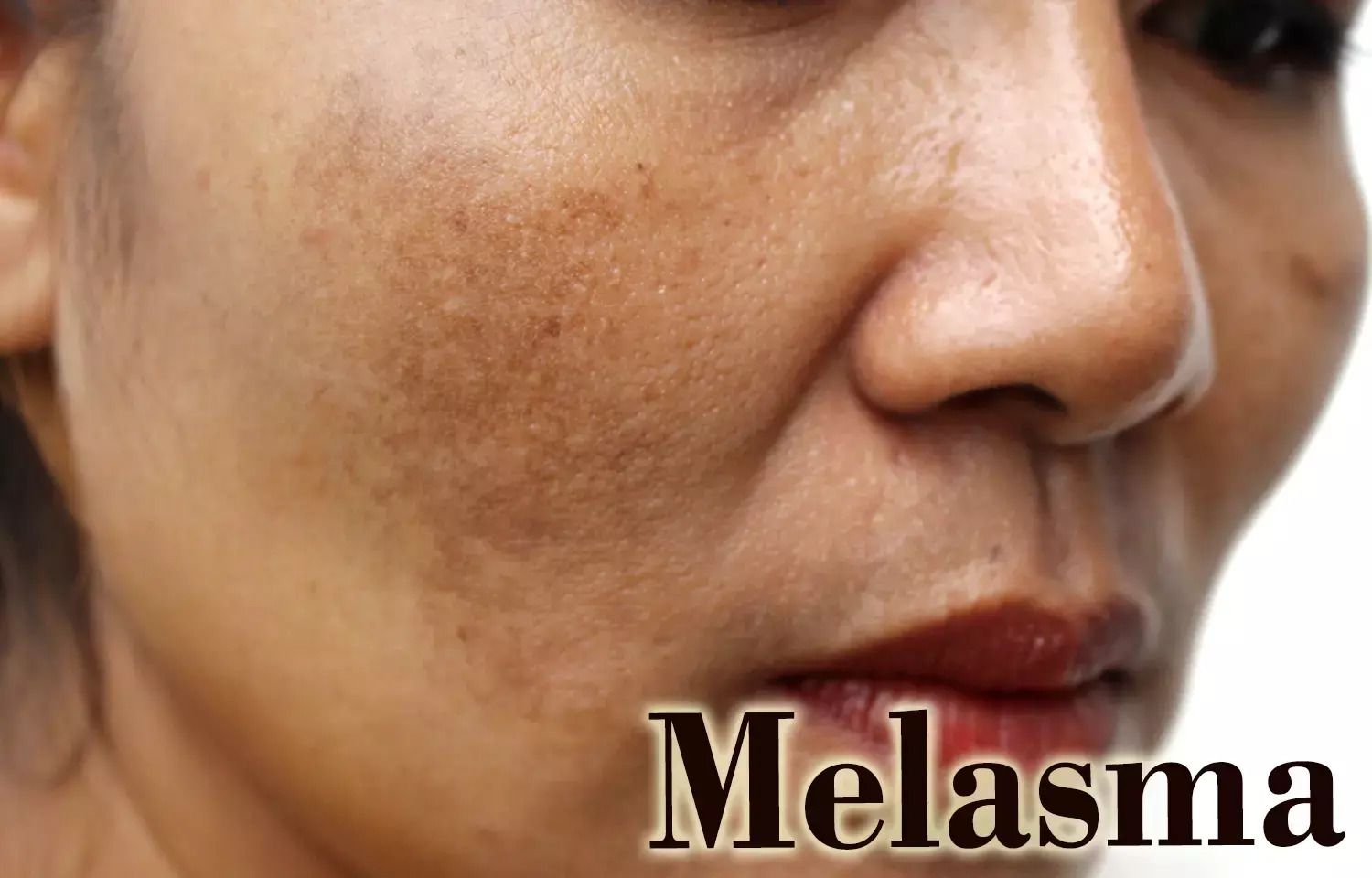
Platelet-rich plasma shows efficacy in melasma- a review. Melasma is an acquired pigmentary disorder primarily occurring over the face that is more prevalent in females and darker skin types. It is predominantly attributed to ultraviolet (UV) exposure and hormonal influences. The estimated prevalence of melasma in the general population is found to be 1%.2 It is usually refractory to treatment. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an autologous blood that has been used in dermatology for facial rejuvenation, androgenetic alopecia, acne scars, and wound healing. Its efficacy has been reviewed recently in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Material and methods:
-
An extensive systematic literature search of the PubMed and Cochrane database were done. All studies and case reports using PRP in the treatment of melasma alone or in combination with other therapies were included. Of the 10 articles found, 6 articles were reviewed and 4 were excluded. Data was analyzed by two different authors.
Procedure
For each session, the face is cleaned with an alcohol gauze. topical eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine (prilox), is applied under occlusion and kept there for an hour before the procedure. Then the face is cleaned and PRP is injected intralesionally at the site of patches of melasma using a 30G hypodermic needle through an insulin syringe. A maximum of 2.0 ml of PRP is injected into the dermis about 1 cm apart to raise dermal papules. Three such sessions of therapy are usually instituted in each patient at an interval of 1 month. Patients are advised to defer from use of any other topical agents which may interfere with the therapeutic outcome.
Important points about PRP preparation-
- In practice the most efficacious concentration of PRP has been found to be 2.5 times the baseline and higher concentrations have not been found to be more efficacious.
- an ideal PRP should have appropriate number of monocytes and T lymphocytes and minimum no neutrophils.
- Role of activation of PRP before injection is not clear
- Acid citrate dextrose and sodium citrate are the most commonly used anticoagulants. Ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid and lithium heparin should be avoided as they deform the morphology of the platelets.
Mechanism of effect in melasma
Alpha-granules pf platelets degranulate to release about 30 growth factors such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). TGF-β1 inhibits melanogenesis by causing reduction in the production of tyrosinase-related protein 1, tyrosinase and tyrosinase-related protein 2. EGF to inhibit prostaglandin-E2 (PGE2) expression and tyrosinase enzyme activity, thus lowering melanin production.
All studies showed a good efficacy of PRP in melasma with minimal side effects and at the same time improve the texture of the skin.1 Thus PRP can be a potentially effective therapy for melasma both as sole treatment or in combination with other therapies.
Source-
- Tuknayat A, Bhalla M, Thami GP. Platelet-rich plasma is a promising therapy for melasma. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Aug;20(8):2431-2436. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14229. Epub 2021 Jun 3. PMID: 34013618.
- Ogbechie-Godec, O. A., & Elbuluk, N. (2017). Melasma: an Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review. Dermatology and therapy, 7(3), 305–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-017-0194-1
MBBS
Dr Manoj Kumar Nayak has completed his M.B.B.S. from the prestigious institute Bangalore medical college and research institute, Bengaluru. He completed his M.D. Dermatology from AIIMS Rishikesh. He is actively involved in the field of dermatology with special interests in vitiligo, immunobullous disorders, psoriasis and procedural dermatology. His continued interest in academics and recent developments serves as an inspiration to work with medical dialogues.He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


