- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ritlecitinib and brepocitinib improve scalp alopecia areata biomarkers: Study
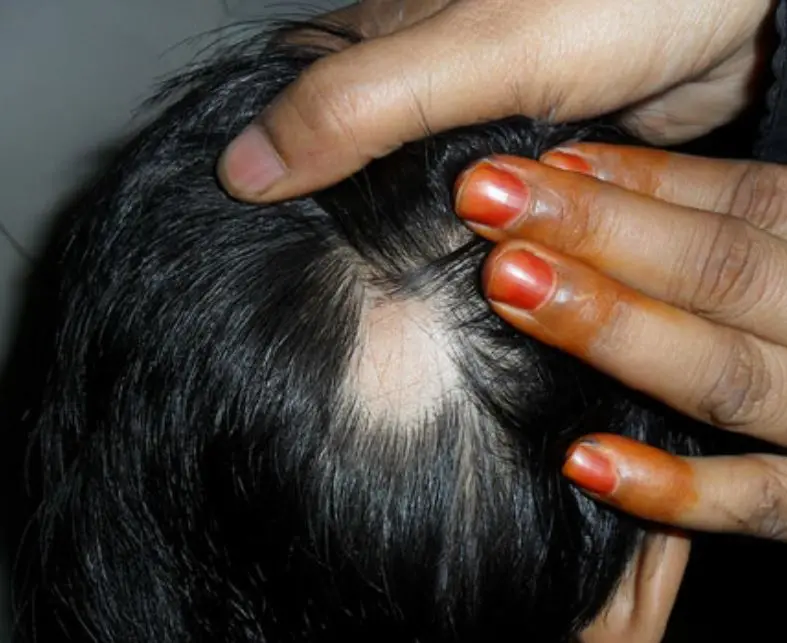
Source- Sacchidanand, Sarvajnamurthy & Srinivas, Sahana & Asha, G & Shilpa, Kanathur. Pattern of Pediatric Dermatoses at a Referral Centre. Indian journal of pediatrics.2012;81:10.1007/s12098-012-0904-8.
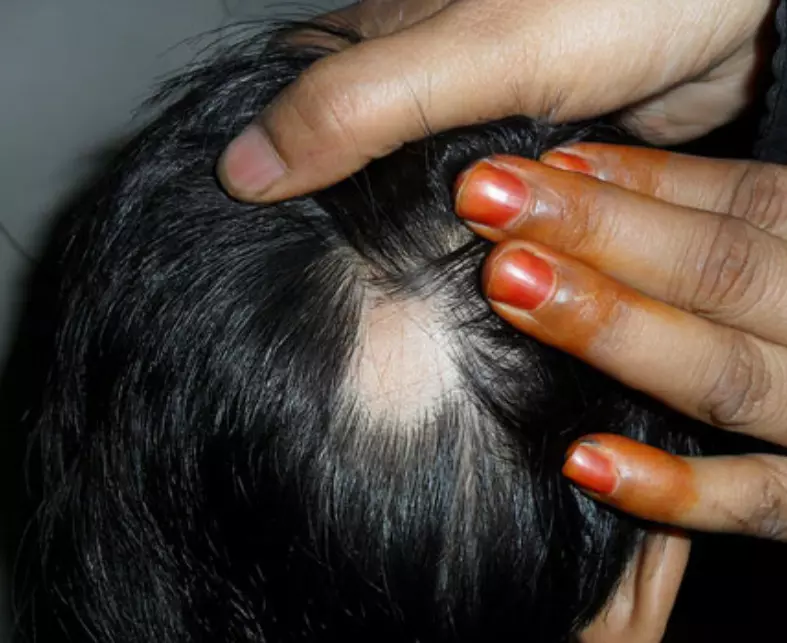
USA: Ritlecitinib and brepocitinib both showed an significant improvement in scalp alopecia areata (AA) biomarkers, finds a recent study.
According to the study which was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, improvement in the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores was positively associated with expression of Th1 markers for both ritlecitinib and brepocitinib and negatively associated with expression of hair keratins. In simpler words, for patients with alopecia areata (AA) treatment with ritlecitinib and brepocitinib associated with improvements in the lesional scalp transcriptome.
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for the treatment of alopecia areata have shown encouraging results in small, uncontrolled studies and case reports. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss. Emma Guttman-Yassky, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, and colleagues conducted a biopsy sub-study during the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled first 24 weeks of a phase 2a clinical trial. The biopsy sub-study evaluated the efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib, an inhibitor of JAK3 and the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) kinase family, and brepocitinib, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2)/JAK1 in the treatment of AA.
The study included 46 patients participated 18 from ritlecitinib, 16 from brepocitinib, and 12 from placebo groups. Change in biomarkers in lesional scalp biopsies between baseline and weeks 12 and 24 was an exploratory endpoint. The researchers also evaluated correlations of biomarkers with hair regrowth, measured using the SALT.
Key findings include:
· At week 24, both ritlecitinib and brepocitinib demonstrated improvement exceeding 100% in the lesional scalp transcriptome toward a nonlesional profile.
· At week 12, the improvements in scalp tissue were greater with brepocitinib than ritlecitinib; however, at week 24, the improvements were greater with ritlecitinib.
"For both ritlecitinib and brepocitinib, improvement in the SALT scores was positively associated with expression of Th1 markers and negatively associated with expression of hair keratins," wrote the authors. "Larger, long-term clinical trials are warranted."
Reference:
The study titled, "Ritlecitinib and brepocitinib demonstrate significant improvement in scalp alopecia areata biomarkers," was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2021.10.036
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


