- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Wound infections more common on lips and lower extremities after skin surgery
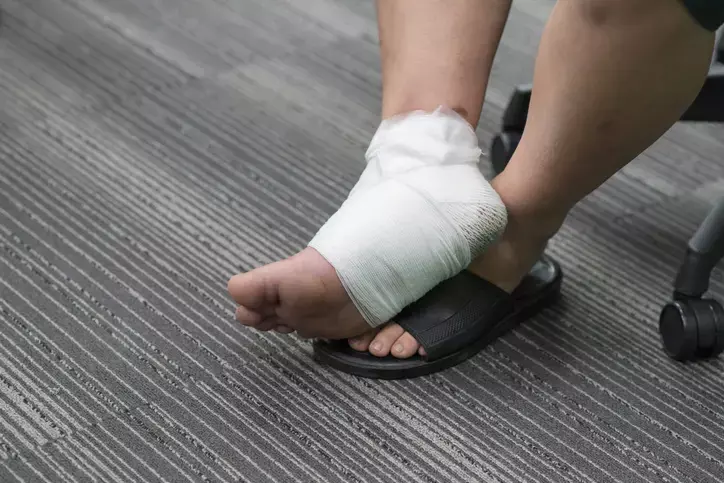
In a new study conducted by Justin Gabriel Schlager and team it was found that after skin surgery, wound infection may be more common on the lips, lower extremities, and maybe the ears and hands. Moreover, the trunk had the least amount of infection. The findings of this study were published in Journal of Dermatologic Surgery.
Identifying wound infection risk variables should help clinicians make the best usage of perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in dermatologic surgery. As a result, this study was carried out to synthesize the available information on whether certain body areas are more susceptible to surgical site infections (SSI).
Embase, MEDLINE, CENTRAL, and trial registrations were all used in the systematic literature search. Only observational studies and meta-analyses were eligible for inclusion. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale was used by the researchers to measure the risk of bias.
The key findings of this study were as follow:
1. There were eighteen studies with a total of 33,086 surgical wounds that were considered.
2. Eight studies were of excellent quality, four were of acceptable quality, and six were of poor quality.
3. The infection rate was 4.08% on average.
4. Lips had much higher infection rates, according to a meta-analysis.
5. Although studies were clinically varied, the lower extremities and ears had or seemed to have a greater risk of infection.
6. Surgical wounds on the hands were shown to be more susceptible to infection in a large prospective experiment.
7. The trunk had the least amount of infection.
8. Because of significant variability across studies, the risk of SSI in other body areas was not different or remained unknown.
In conclusion, the findings of this study is a clear indication of the surgical scar, where following skin surgery, lower extremities, the lips, ears, and hands had the greatest rates of infection, whereas the trunk had the lowest. Therefore, surgeon should keep this in mind when performing surgery in various body parts.
Reference:
Schlager, J. G., Ruiz San Jose, V., Patzer, K., French, L. E., Kendziora, B., & Hartmann, D. (2022). Are Specific Body Sites Prone for Wound Infection After Skin Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. In Dermatologic Surgery (Vol. 48, Issue 4, pp. 406–410). Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000003387
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


