- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Nifedipine CR and sacubitril valsartan combo alleviates progression of diabetic nephropathy with hypertension
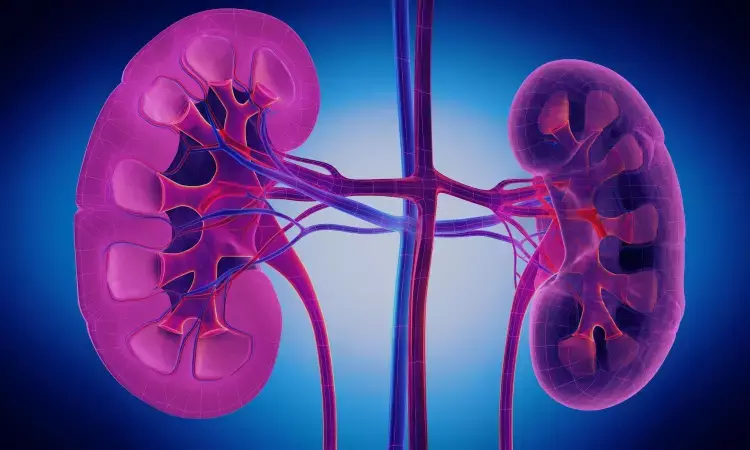
China: A recent study published in International Immunopharmacology by Yinyu Wei and colleagues showcases the efficacy of a combination of nifedipine controlled-release tablets and sacubitril valsartan in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN) accompanied by hypertension. With over a hundred participants, this prospective randomized controlled study aims to shed light on a potential treatment approach for this often intricate health concern.
The study enrolled 112 participants with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) exceeding six years. Randomly divided into two groups, the participants underwent different treatment regimens. One group received nifedipine-controlled-release tablets combined with valsartan, while the other received nifedipine-controlled-release tablets combined with sacubitril valsartan.
- The results showcased that after a three-month treatment period, the observation group (nifedipine controlled-release tablets combined with sacubitril valsartan) exhibited significantly lower levels of various clinical indices, renal function indicators, endothelial function indicators, and inflammatory response factors compared to the control group.
- Glycosylated haemoglobin, fasting blood glucose, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and other key parameters experienced a reduction in the observation group.
Diabetic nephropathy is a frequent complication of type 2 diabetes, often aggravated by hypertension. In this study, the combination of nifedipine and sacubitril valsartan proved to be promising in addressing the intricate health concerns associated with these conditions. The treatment showcased improvements in renal and endothelial function, reducing inflammation and positively influencing clinical indicators.
The study's outcomes indicate that the combination of nifedipine controlled-release tablets and sacubitril valsartan presents a potential avenue to alleviate the progression of diabetic nephropathy in the presence of hypertension. With favourable outcomes and minimal adverse effects, this approach offers a glimpse of hope for individuals grappling with these complex health issues. As researchers delve deeper into this treatment approach, further investigations and clinical trials are warranted to validate its efficacy and safety.
Reference:
Wei, Y., Hu, L., & Liu, G. (2023). Therapeutic improvements of nifedipine controlled-release tablets combined with sacubitril valsartan on patients with diabetic nephropathy complicated with hypertension. International Immunopharmacology, 123(110755), 110755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110755
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


