- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Probiotics combined with exercise significantly improve liver enzymes, lipid profile and insulin resistance in NAFLD patients: Study
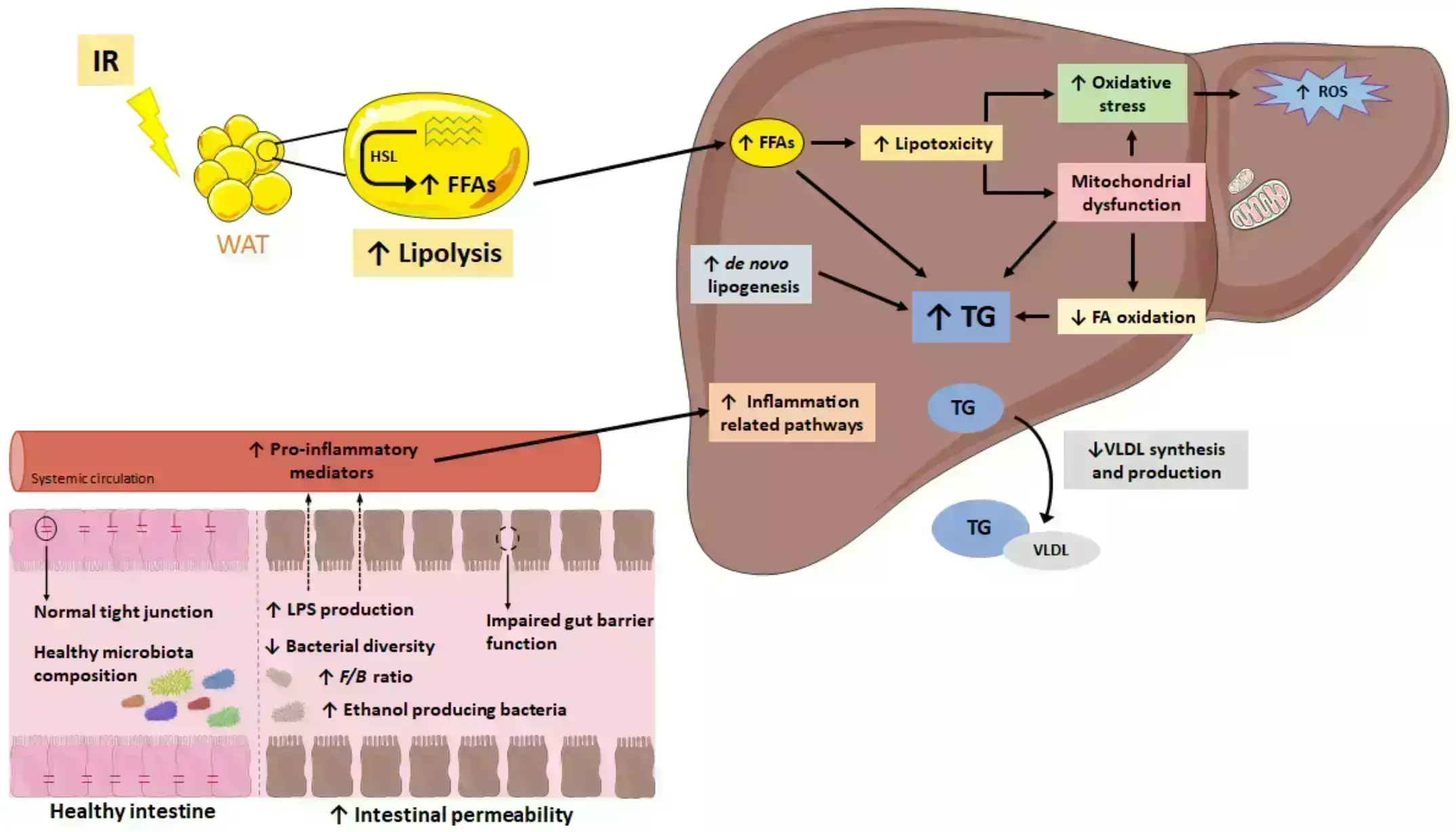
Probiotics combined with exercise significantly improve liver enzymes, lipid profile and insulin resistance in NAFLD patients suggests a study published in the Nutrition & Metabolism.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver ailment worldwide, in which nonpharmacological strategies have a considerable role in the treatment. Probiotic supplementation as well as physical exercise can improve cardiometabolic parameters, but further research is needed to determine the effects of combined treatment versus exercise alone in managing NAFLD-associated biomarkers, primarily liver enzymes, lipid markers, and insulin resistance. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effects of probiotic supplementation, combined with exercise versus exercise alone, on liver enzymes and cardiometabolic markers in patients with NAFLD. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials was performed by searching PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases up to April 2024. The search was restricted to articles published in the English language and human studies. Random effects models were used to calculate weighted mean differences (WMD). Results: Pooled estimates (9 studies, 615 patients, intervention durations ranging from 8 to 48 weeks) revealed that probiotics plus exercise decreased aspartate transaminase (AST) [WMD=-5.64 U/L, p = 0.02], gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) [WMD=-7.09 U/L, p = 0.004], low-density lipoprotein (LDL) [WMD=-8.98 mg/dL, p = 0.03], total cholesterol (TC) [WMD=-16.97 mg/dL, p = 0.01], and homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) [WMD=-0.94, p = 0.005] significantly more than exercise only.
However, probiotics plus exercise did not significantly change high-density lipoprotein (HDL) [WMD = 0.07 mg/dL, p = 0.9], fasting insulin [WMD=-1.47 µIU/mL, p = 0.4] or fasting blood glucose (FBG) [WMD=-1.57 mg/dL, p = 0.3] compared with exercise only. While not statistically significant, there were clinically relevant reductions in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) [WMD=-6.78 U/L, p = 0.1], triglycerides (TG) [WMD=-21.84 mg/dL, p = 0.1], and body weight (BW) [WMD=-1.45 kg, p = 0.5] for probiotics plus exercise compared with exercise only. The included studies exhibited significant heterogeneity for AST (I2 = 78.99%, p = 0.001), GGT (I2 = 73.87%, p = 0.004), LDL (I2 = 62.78%, p = 0.02), TC (I2 = 72.41%, p = 0.003), HOMA-IR (I2 = 93.86%, p = 0.001), HDL (I2 = 0.00%, p = 0.9), FBG (I2 = 66.30%, p = 0.01), ALT (I2 = 88.08%, p = 0.001), and TG (I2 = 85.46%, p = 0.001). There was no significant heterogeneity among the included studies for BW (I2 = 0.00%, p = 0.9). Probiotic supplementation combined with exercise training elicited better results compared to exercise alone on liver enzymes, lipid profile, and insulin resistance in patients with NAFLD.
Reference:
Kazeminasab, F., Miraghajani, M., Mokhtari, K. et al. The effects of probiotic supplementation and exercise training on liver enzymes and cardiometabolic markers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutr Metab (Lond) 21, 59 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-024-00826-8
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


