- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Reliable Sampling Techniques are Crucial for COVID Nasal Swab Test: JAMA
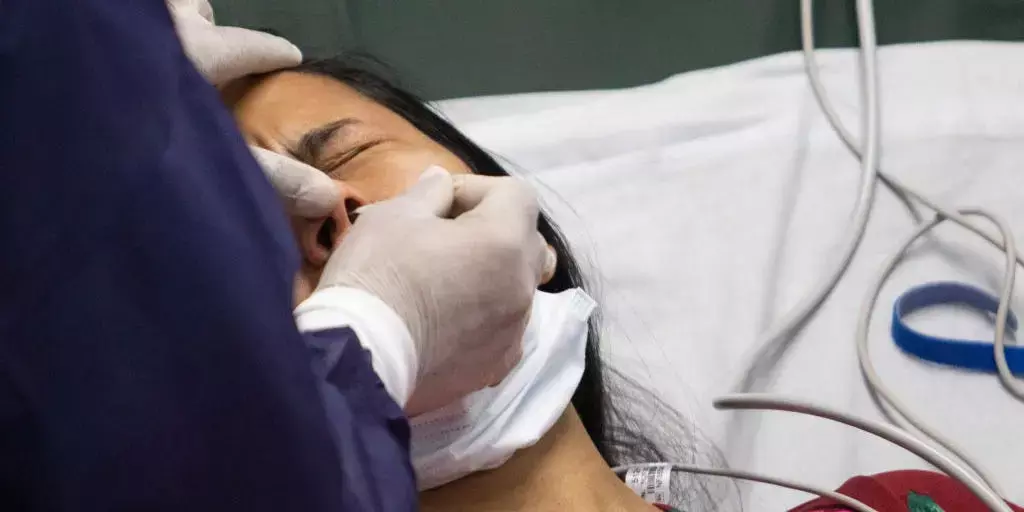
CDC (Centres for Disease Control and Prevention) recommends that anyone with any signs or symptoms of COVID-19 get tested, regardless of vaccination status or prior infection. Nasal swab RT-PCR testing is the most commonly used for diagnosing air-borne disease and, it has excellent specificity and sensitivity in detecting the SARS-CoV-2 virus within 48 hours. Although complications are rare, their frequency and causes remain unclear. For the same, a research team conducted a case series study and emphasized the importance of adequately trained technicians who can perform nasal swabs for Covid-19 RT-PCR tests safely. The research has been published in the JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery on April 29, 2021.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, numerous swab samples have been taken for SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing. Nasopharyngeal sampling is considered safe, despite adjacent vital structures (eg orbit, skull base, rich vasculature). However, single case reports and clinical observations indicate the possibility of severe complications. Therefore, researchers of the University of Helsinki, Finland, conducted a study to investigate the frequency and type of SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal test complications.
In this 7 month, retrospective case series study, researchers evaluated patients for complications after SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab sampling. Around 6,43,284 Covid-19 RT-PCR tests were performed within seven months. They reviewed medical records of patients who experienced complications after sampling. They also got the number of Covid-19 tests performed in the Helsinki University hospital (1.6 million) during the same period from the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare.
Key findings of the study were:
- Among 643 284 SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR tests, the researchers observed eight complications related visits in the emergency department.
- Among 8 patients, 4 had nasal bleeds and, 4had broken swabs, all occurring immediately after sampling. However, they noted that none of these 8 patients tested positive for COVID-19.
- They found that the frequency of complications requiring treatment in the ED was 1.24 per 100 000 performed SARS-CoV-2 tests.
- They noted that the broken swabs were removed via nasal endoscopy under local anaesthesia, whereas the nasal bleeds required medication, numerous nasal packings, and surgical and endovascular procedures and led to fetal risk, sepsis, and blood transfusions.
- They also noted that half of the bleeds were potentially life-threatening (haemoglobin level fell below 6.5 g/dL [to convert to g/L, multiply by 10.0]).
- They reported that massive bleeding complicated the localization of the bleeds.
- They noted that repetitive nasal packings might cause infections, transnasal adhesions and septal perforations.
However, they reported that the rate of complications was low and said, "All complications seemed to involve an incorrect sampling technique: excess use of force or an overly cranial direction of the swab. "
They recommended,
♦ "Sampling should always be performed bearing in mind the anatomical structures of the nasal cavity and its surroundings to ensure safe sampling and correct results.
♦ Force should never be used, especially in patients with known prior operations of the nose or skull base.
♦ The sampling swab should be directed along the nasal floor, not too laterally nor too cranially until resistance is encountered."
The authors concluded, "Based on the results, the risk for a severe complication requiring specialist-level care after SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab testing is extremely low. Nonetheless, complications involve anatomically challenging locations and may be life-threatening. To avoid complications, correct sampling techniques are crucial."
For further information:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2779393
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


