- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Non-Antibiotic Outpatient Treatment effective for Mild Acute Diverticulitis: Study
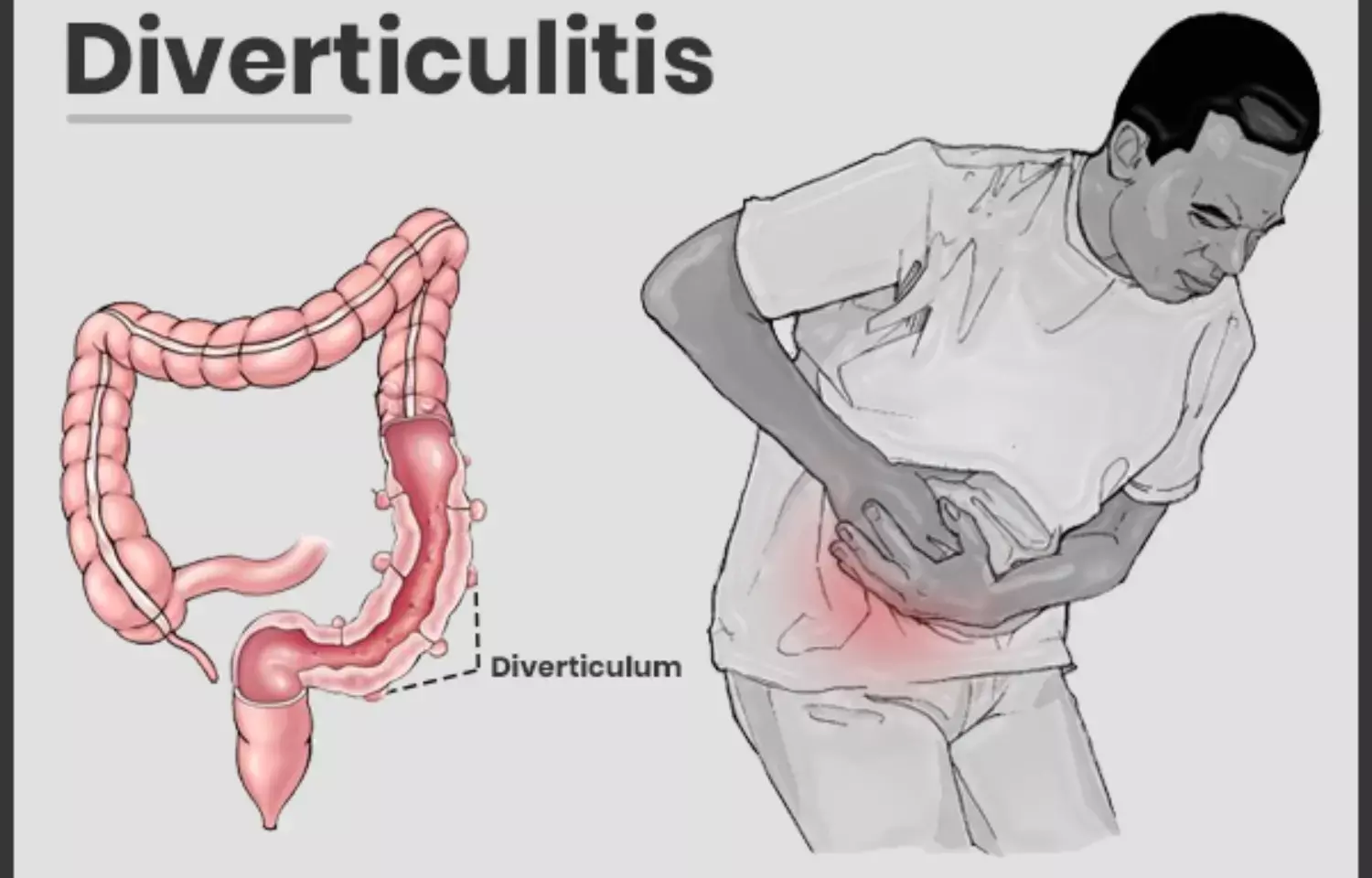
Non-antibiotic outpatient treatment of mild Acute Diverticulitis is safe and has a similar efficacy profile as the present routine treatment, suggests a study published in the Annals of Surgery.
Diverticulitis refers to the "inflammation and infection of" one or more diverticula, which are the bulges in the colon wall. The most common treatment modality for mild diverticulitis is antibiotics. However, lately, antibiotics have proven ineffective in treating uncomplicated acute diverticulitis especially in the patients admitted in hospitals, while on the contrary the outpatient care of the same patients has been comparatively safer and more effective.
A study was conducted by Laura M et. al to demonstrate if on an outpatient basis, Mild acute diverticulitis (AD) can be managed safely and effectively without the use of antibiotics.
The researchers conducted a prospective, multicentre, open-label, non-inferiority, randomized controlled trial, in the emergency wards of over 15 hospitals where patients with symptoms of acute diverticulitis as diagnosed by CT scan were included.
A total of 480 patients were then randomized to either a control group (ATB-Group; n = 238): classical treatment (875/125 mg/8 h amoxicillin/clavulanic acid apart from anti-inflammatory and symptomatic treatment) or experimental group (Non-ATB-Group; n= 242): experimental treatment (anti-inflammatory and symptomatic treatment). Clinical controls were performed at 2, 7, 30, and 90 days.
The primary endpoint was hospital admission, while the secondary endpoints included a number of emergency department revisits, pain control and emergency surgery in the different arms.
The findings of the study are as follows:
· The hospitalization rats were more in the ATB group (5.8%) as compared to the Non-ATB group (3.3%)
· Hospital revisits in both the groups were almost the same; ATB group (6.7%) and Non-ATB group (7%)
· While for poor pain control at 2 days follow up was worse in the ATB-Group (5.7%) as compared to the Non-ATB-Group (2.3%)
The researchers concluded that non-antibiotic outpatient treatment for mild Acute Diverticulitis is also safe and equally effective when compared with the current standard treatment.
Reference:
Efficacy and Safety of Non-Antibiotic Outpatient Treatment in Mild Acute Diverticulitis (DINAMO-study): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label, Non-Inferiority Trial by Laura M et. al in the Annals of Surgery.
DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005031
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


