- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Steroids effective in Severe COVID-19 patients with high serum ferritin levels only: JAMA
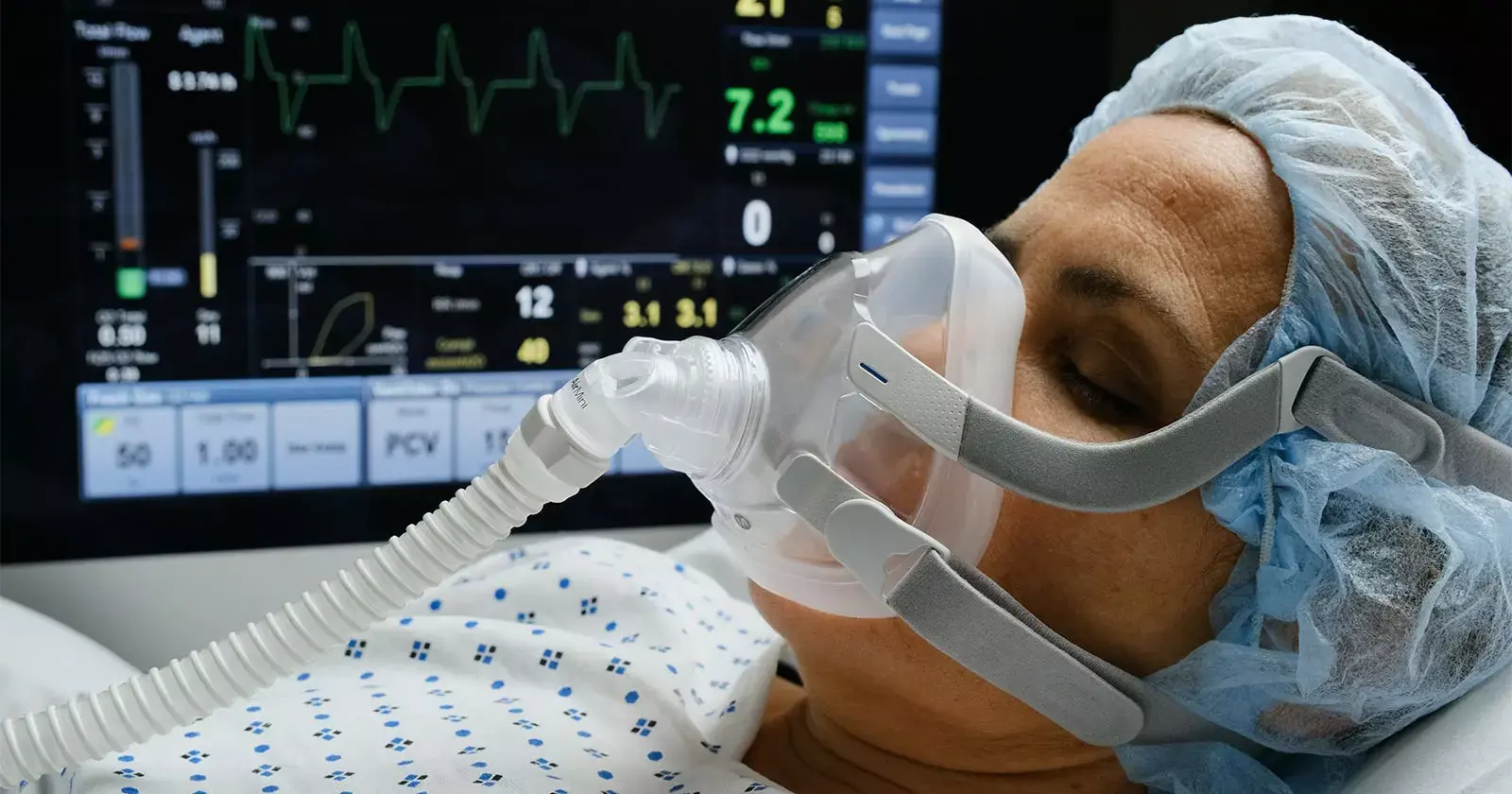
Methylprednisolone therapy in COVID-19 patients receiving high-flow oxygen therapy was associated with clinical benefit mainly in patients with baseline serum ferritin levels in the upper tertile of values, find researchers.
These findings suggest that ferritin levels on admission may be used as a marker associated with corticosteroid response among patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia.
The study is published in the JAMA Network Open.
Serum ferritin, an acute phase marker of inflammation, has several physiologic functions, including limiting intracellular oxidative stress. Whether the effectiveness of corticosteroids differs according to serum ferritin level in COVID-19 has not been reported.
A group of researchers conducted a study to examine the association between admission serum ferritin level and methylprednisolone treatment outcomes in non-intubated patients with severe COVID-19.
This retrospective cohort study included patients with severe COVID-19 admitted to an academic referral center in Stony Brook, New York, from March 1 to April 15, 2020, receiving high-flow oxygen therapy. The outcomes of treatment with methylprednisolone were estimated using inverse probability of treatment weights, based on a propensity score comprised of clinical and laboratory variables. Patients were followed up for 28 days. Data were analyzed from December 19, 2020, to July 22, 2021.
The results of the study are as follows:
· Among 380 patients with available ferritin data, 142 patients (37.4%) received methylprednisolone.
· Ferritin levels were similar in patients who received methylprednisolone vs those who did not.
· In weighted analyses using tertiles of ferritin values, methylprednisolone was associated with lower mortality in patients with ferritin in the upper tertile and higher mortality in those with ferritin in the middle and lower tertiles.
· Composite end point rates were lower with methylprednisolone in patients with ferritin in the upper tertile but not in those with ferritin in the middle and lower tertiles.
Thus, the researchers concluded that in this cohort study of nonintubated patients with severe COVID-19, methylprednisolone was associated with improved clinical outcomes only among patients with admission ferritin in the upper tertile of values.
Reference:
Association of Serum Ferritin Levels and Methylprednisolone Treatment with Outcomes in Non-intubated Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia by Papamanoli A et. al published in the JAMA Netw Open.
doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27172
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


