- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
IV alteplase use fails to improve functional outcomes in patients with ICH and IVH: JAMA
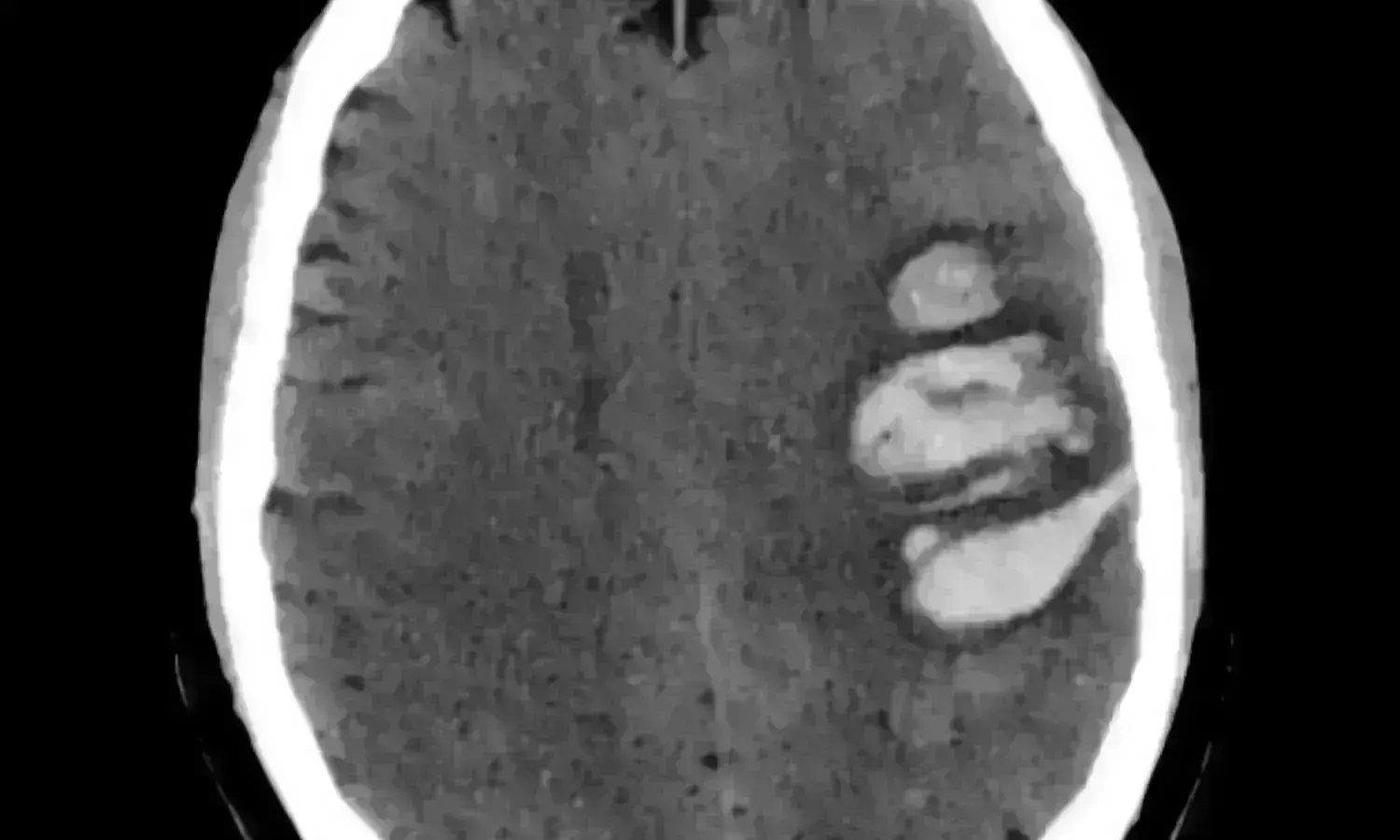
USA: Intraventricular alteplase use is associated with a small reduction in the parenchymal intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) volume in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), suggests a recent study. However, the researchers observed no association between change in ICH volume and improved functional outcomes or mortality. The study was published in JAMA Network Open on December 3, 2021.
Intraventricular thrombolysis is known to reduce IVH volume in patients with spontaneous ICH. However, if there is existence of a similar association with parenchymal ICH volume remains unclear. To throw some light on the association, Jens Witsch, Department of Neurology, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the association between the use of intraventricular alteplase and ICH volume as well as the association between a change in parenchymal ICH volume and long-term functional outcomes in a cohort study.
The study was a post hoc exploratory analysis of data from the Clot Lysis: Evaluating Accelerated Resolution of Intraventricular Hemorrhage phase 3 randomized clinical trial with blinded outcome assessments. Patients with ICH with IVH and ICH were randomized to receive either intraventricular alteplase or normal saline via an external ventricular drain between September 1, 2009, and January 31, 2015. Participants with primary IVH were excluded.
The primary outcome was the change in parenchymal ICH volume between the hematoma stability and end-of-treatment computed tomography scans.
Out of the total 454 included patients (254 men [55.9%]; mean age, 59 years), 230 (50.7%) were randomized to receive alteplase and 224 (49.3%) to receive normal saline.
The study revealed the following:
- The alteplase group had a greater mean reduction in parenchymal ICH volume compared with the saline group (1.8 mL vs 0.4 mL).
- In the primary analysis, alteplase use was associated with a change in the parenchymal ICH volume in the unadjusted analysis per 1-mL change (β, 1.37) and in multivariable linear regression analysis that was adjusted for demographic characteristics, stability ICH and IVH volumes, ICH location, and time to the first dose of study drug per 1-mL change (β, 1.20).
- In the secondary analyses, no association was found between change in parenchymal ICH volume and poor outcome (odds ratio [OR], 0.97) or mortality (OR, 0.97). Similar results were observed in the subgroup analyses.
"The study findings suggest the need for further exploration of the role of intraventricular thrombolysis in reducing parenchymal ICH volumes and potentially improving outcomes in patients with a moderate to large ICH with IVH and those with a thalamic ICH," wrote the authors.
"Examining patients with ICH and IVH who may benefit from intraventricular thrombolysis, such as those with moderate to large ICH in thalamic location, may yield useful information," they concluded.
Reference:
Witsch J, Roh DJ, Avadhani R, et al. Association Between Intraventricular Alteplase Use and Parenchymal Hematoma Volume in Patients With Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Intraventricular Hemorrhage. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(12):e2135773. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.35773
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


