- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Myo-inositol found in breast milk may enhance neuronal connectivity in brain of infants
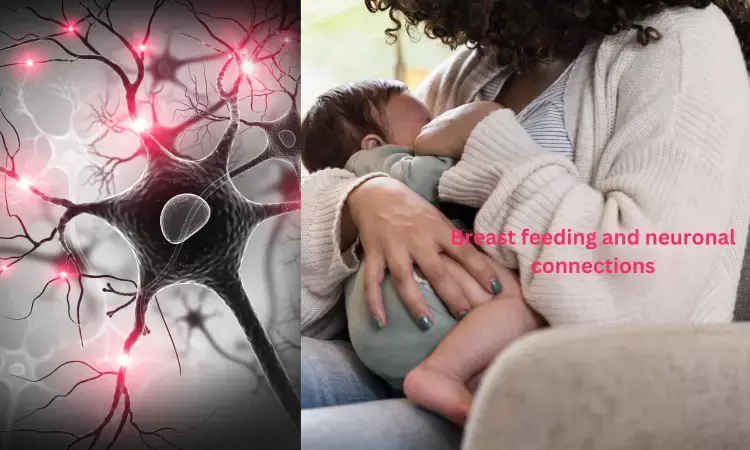
Breast feeding is long known for its ideal nutrition for infants. It has a nearly perfect mix of vitamins, protein, and fat that baby needs to grow. Breast milk contains antibodies that help baby build a better immune system. Breastfeeding is also said to lower baby's risk of having asthma or allergies. Breastfeeding has been linked to higher IQ scores in later childhood in some studies.
The present study in PNAS Journal reveals substantial benefits of the human milk component myo-inositol for developing synapses across species, including in human neurons. The findings demonstrated that myo-inositol promotes neuronal connectivity and can guide dietary recommendations across life stages.
This is a significant finding for pediatric nutrition and the improvement of infant formulas in under resourced areas with conditions that prevent sufficient breastfeeding. Moreover, this carbocyclic sugar can promote synapse density in mature brain tissue.
The researchers aimed to know the effects of micronutrients on brain connectivity. The researchers studied samples from three geographically diverse locations because they hypothesized that the micronutrients present across all samples—independent of diet, race, and location—may be of biological significance. They were especially interested in components that changed over the course of lactation in the same way.
The key findings of the study are
• The researchers determined that Myo-inositol is most abundant in human milk during early lactation when neuronal connections rapidly form in the infant brain.
• Myo-inositol promoted synapse abundance in human excitatory neurons as well as cultured rat neurons and acted in a dose-dependent manner.
• Mechanistically, myo-inositol enhanced the ability of neurons to respond to transsynaptic interactions that induce synapses.
• Effects of myo-inositol in the developing brain were tested in mice, and its dietary supplementation enlarged excitatory postsynaptic sites in the maturing cortex.
• Utilizing an organotypic slice culture system, they additionally determined that myo-inositol is bioactive in mature brain tissue, and treatment of organotypic slices with this carbocyclic sugar increased the number and size of postsynaptic specializations and excitatory synapse density.
Researchers concluded that “This study advances our understanding of the impact of human milk on the infant brain and identifies myo-inositol as a breast milk component that promotes the formation of neuronal connections.”
Reference: Dhrubajyoti Chowdhury, Ilona Kondratiuk, Beau Labhart et al; The human milk component myo-inositol promotes neuronal connectivity, PNAS Journal Article, 2023 vol 30; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2221413120.
MSc. Neuroscience
Niveditha Subramani a MSc. Neuroscience (Faculty of Medicine) graduate from University of Madras, Chennai. Ambitious in Neuro research having worked in motor diseases and neuron apoptosis is interested in more of new upcoming research and their advancement in field of medicine. She has an engrossed skill towards writing and her roles at Medical dialogue include Sr. Content writer. Her news covers new discoveries and updates in field of medicine. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


