- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rapid administration of undiluted intravenous levetiracetam considered safe: Study
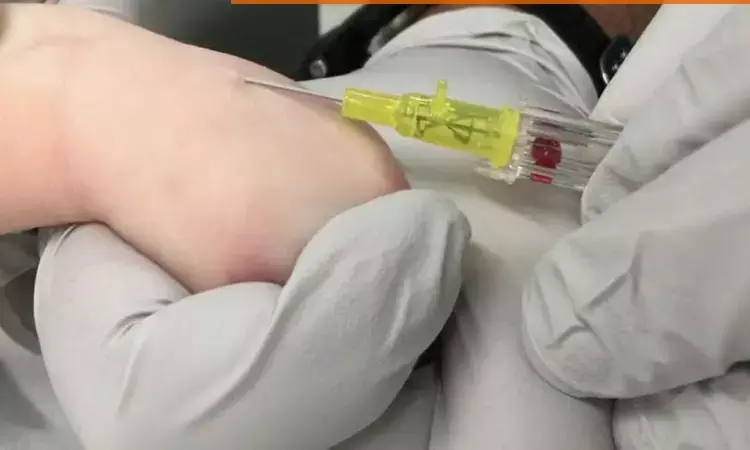
Operational delays have the potential to lead to suboptimal time to seizure control during status epilepticus. Levetiracetam (LEV) is an urgent control antiepileptic medication that offers relative lack of adverse effects and ease of monitoring.
There are limited data published demonstrating safety and tolerability of undiluted rapid intravenous (IV) push of LEV in doses of 1000 mg or less. However, rapid IV administration of undiluted LEV is both safe and tolerable in doses of up to 4500 mg, allowing for rapid drug administration, finds a study.
The research is published in the Epilepsia Journal.
John Tyler Haller and colleagues from the Department of Pharmacy, St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA evaluated the safety of IV push administration of LEV doses up to 4500 mg.
The authors carried out a retrospective, observational, cohort analysis of adult patients who received at least one dose of undiluted IV push LEV at a large academic medical center in Phoenix, Arizona. Outcomes of interest include safety and tolerability of rapid administration of undiluted LEV.
The results of the study revealed that-
a. There were 953 unique patients included during the study period.
b. LEV was a new medication for witnessed or suspected seizure in 51.9% of patients, and 40.7% of patients had a documented history of epilepsy or seizure disorder.
c. There were 8561 undiluted IV push LEV doses administered, 3674 (42.9%) of which were greater than 1000 mg.
d. LEV was administered most often through a peripheral IV (79.1%).
e. There were 12 patients with documented adverse drug events during the study period, with four potentially directly related to IV push LEV administration.
f. These events were limited to local injection site reactions and included redness, burning, and loss of a peripheral IV line.
Hence, the authors concluded that "rapid IV administration of undiluted LEV is both safe and tolerable in doses of up to 4500 mg, allowing for rapid drug administration, which is paramount during neurologic emergencies."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


