- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Endosalpingiosis linked with increased risk of cancer risk compared to endometriosis
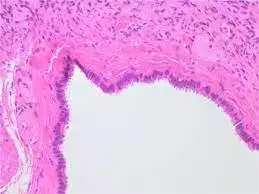
Endosalpingiosis is an ectopic endothelial abnormality. It is a poorly understood condition of ectopic epithelium resembling the fallopian tubes. It has been described as an incidental pathology finding, a disease similar to endometriosis, and in association with malignancy.
According to a retrospective case-control study endosalpingiosis doubled the risk of concurrent gynecologic malignancy as compared with endometriosis and conferred worse overall survival (OS).
The study has been published in the Gynecologic Oncology.
Endosalpingiosis is a poorly understood condition of ectopic epithelium resembling the fallopian tubes. It has been described as an incidental pathology finding, a disease similar to endometriosis, and in association with malignancy. The objective of this study is to determine if endosalpingiosis (ES) has an increased association with gynecologic malignancy when compared to endometriosis (EM).
This is a retrospective case-control analysis of patients with a histologic diagnosis of endosalpingiosis or endometriosis at three affiliated academic hospitals between 2000 and 2020. All endosalpingiosis patients were included, and 1:1 matching was attempted to obtain a comparable cohort of endometriosis patients. Demographic and clinical data were obtained, and statistical analysis was performed.
The results of the study are:
- A total of 967 patients (515 ES and 452 EM) were included.
- Endosalpingiosis patients were significantly older than endometriosis patients.
- The endosalpingiosis group had significantly more cancer diagnoses at surgery than the endometriosis group; this difference persisted in a sub-analysis excluding patients with known or suspected malignancy.
- Endosalpingiosis patients had lower overall survival.
- After adjusting for confounders, multivariable analysis showed that endosalpingiosis patients had increased cancer diagnosed at surgery and greater risk of death.
Thus, endosalpingiosis was found concurrently with malignancy in 40% of cases, and this effect was preserved in multi-variable and sub-group analyses. Further research consisting of longer follow-up and exploration of molecular relationships between endosalpingiosis and cancer are forthcoming.
Reference:
Gregory K. Lewis et al. The association of endosalpingiosis with gynecologic malignancy Published: July 28, 2022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2022.07.025
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


