- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ultrasound-guided localization with magnetic seeds effective for localizing small non-palpable breast lesions
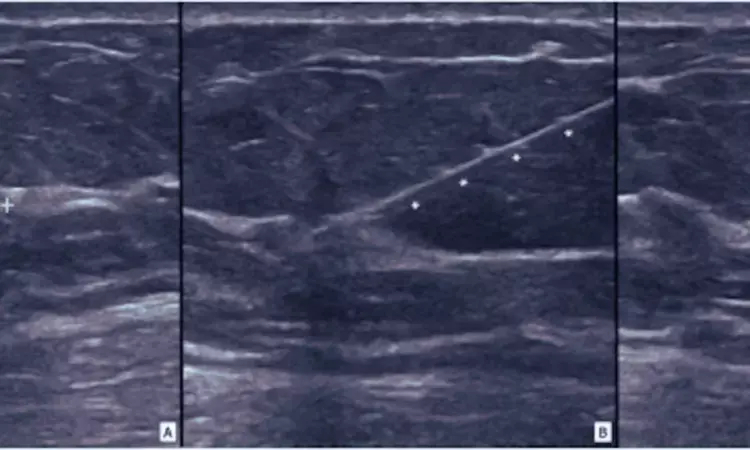
Italy: A recent study published in Clinical Breast Cancer has suggested that image-guided localization with magnetic seeds is a safe, easy, effective, and reliable method for localizing nonpalpable breast lesions. Also, it is shown to perform better than stereotactic seed localization.
"Both surgeons and radiologists agreed that the technology was intuitive to use and could be widely applied in pre-operative localization in breast units," the researchers wrote in their study.
A significant proportion of breast cancer detected at mammographic screening are often small and non-palpable. To avoid excessive tissue removal, there is a need to precisely localize the non-palpable breast cancers before treatment. Wire localization has been the gold standard but researchers have begun experimenting with non-wired methods in recent years. These include magnetic seeds, radiofrequency identification (RFID) tags, radar reflectors, and radioactive seeds.
Catherine Depretto, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale Tumori di Milano, Via Giacomo, Milan, Italy, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the performance of pre-operative magnetic seed localization of non-palpable breast lesions on a large scale.
For this purpose, the researchers prospectively collected data on all patients undergoing image-guided magnetic seed localization from 2019 to 2022. They analyzed the type of surgery, histological results, and imaging findings.
The primary outcome of the study was determined as the successful localization rate. Secondary outcomes included the ease of percutaneous positioning, successful placement rate, reintervention rate, and procedural complications.
The authors reported the following findings:
· A total of 1123 magnetic seeds were placed in 1084 patients by four radiologists under ultrasound (1053) or stereotactic (70) guidance.
· All seeds were detectable transcutaneously in all breast sizes and at all depths by seven surgeons with a success rate of 100%. 97,5% of the seeds were correctly placed into the target lesions (only 2,5% were dislocated).
· All radiologists have shown good compliance during the procedure, and there were no complications or safety issues.
· The re-operation rate was 5,1 %.
According to the authors, "this is the single-centre study with the largest cohort worldwide."
They added, "large size of the patient cohort allows us to add more evidence that image-guided localization with magnetic seeds is a safe, easy, effective, and reliable method for localizing non-palpable breast lesions."
"Consensus between surgeons and radiologists in our study highlighted the intuitive nature of this technology."
"Magnetic seed localization presents a promising avenue for widespread adoption in breast units," they concluded.
Reference:
The study titled, "Magnetic localization of breast lesions: a large-scale European evaluation in a National Cancer Institute," was published in Clinical Breast Cancer.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2023.08.004
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


