- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Abnormal red reflex indicates ocular disease in infants: JAMA
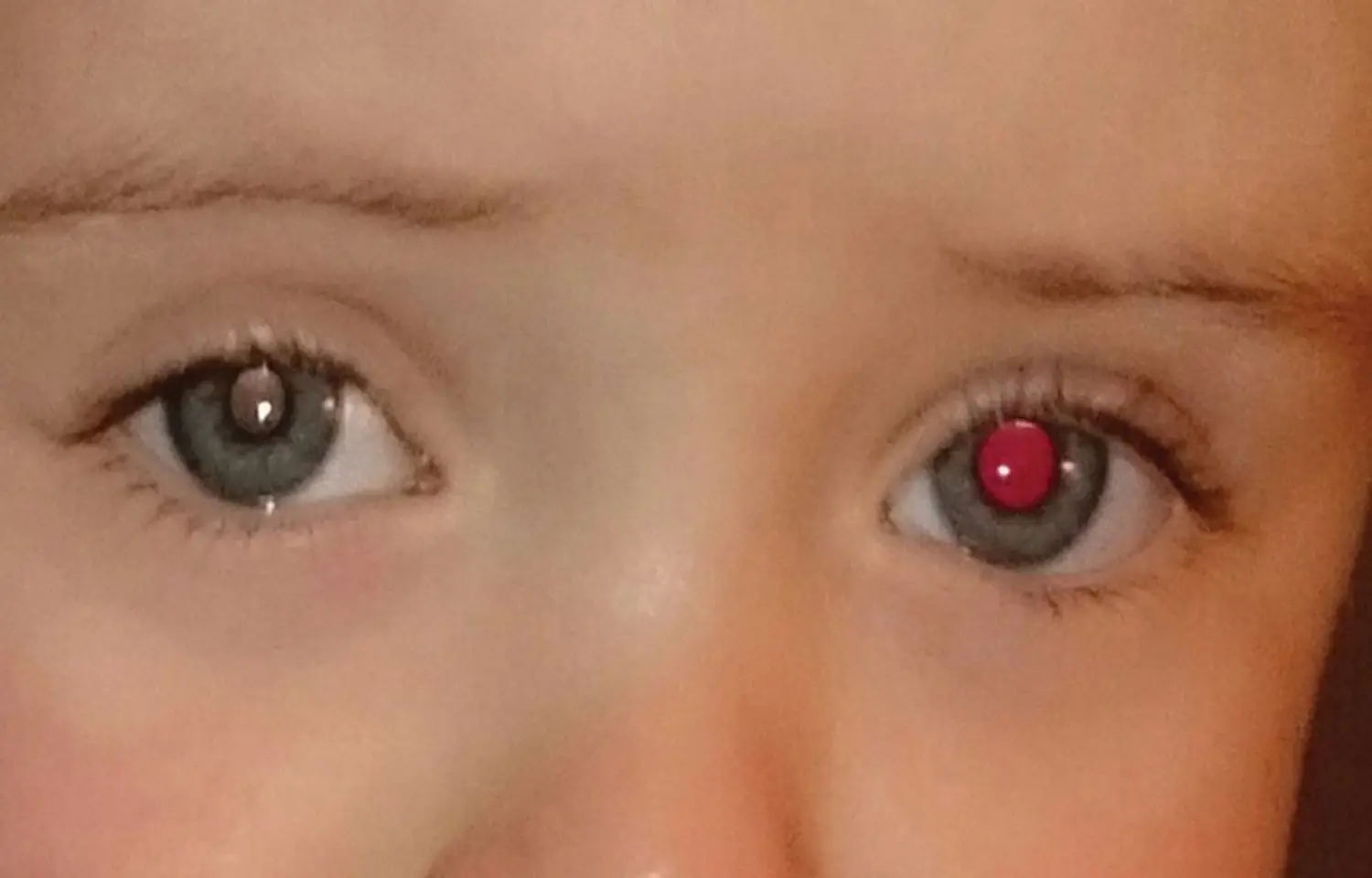
Denmark: A normal red reflex does not exclude ocular disease but an abnormal red reflex most likely reflects an underlying ocular pathology while screening in infants, suggests a recent study in the journal JAMA Ophthalmology.
Red reflex testing is an essential component of the neonatal, infant, and child physical examination according to a joint policy statement by American Association of Certified Orthoptists, the American Academy of Ophthalmology, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, and the American Academy of Pediatrics. It is simple and inexpensive method implemented in many countries as an essential part of infant screening for ocular pathologies.
Yousif Subhi, Department of Ophthalmology, Rigshospitalet-Glostrup, Glostrup, Denmark, and colleagues reviewed the literature on the diagnostic accuracy of the red reflex test in infant screening for ocular pathologies and to perform meta-analyses to provide summary estimates.
The researchers searched the online databases for studies published until April 19, 2020. Eligibility criteria were defined according to population (studies of consecutively screened infants), exposure (red reflex or Brückner test as the index test), comparator (any ophthalmological examination), and study type (any study with diagnostic test accuracy data).
Main outcome measures included true-positive, false-positive, true-negative, and false-negative findings; sensitivity; specificity; and positive and negative predictive values. This meta-analysis included a total of 8713 unique infants from 5 unique studies.
Key findings of the study include:
- All the included studies used the red reflex test without pupillary dilation and were compared with a reference test performed with pupillary dilation.
- For any ocular pathology, an estimated sensitivity of 7.5% and specificity of 97.5% was found.
- Focusing on ocular pathologies that required a medical or surgical intervention, sensitivity improved to 17.5% and specificity remained high at 97.6%.
"Our findings demonstrate that an abnormal red reflex finding most likely reflects an underlying ocular pathology. However, a normal red reflex finding during screening does not exclude ocular disease," concluded the authors.
"Diagnostic Test Accuracy of the Red Reflex Test for Ocular Pathology in Infants: A Meta-analysis," is published in the journal JAMA Ophthalmology.
DOI: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2020.4854
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


