- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intracanalicular Insert of Dexamethasone Effective option for Allergic Conjunctivitis
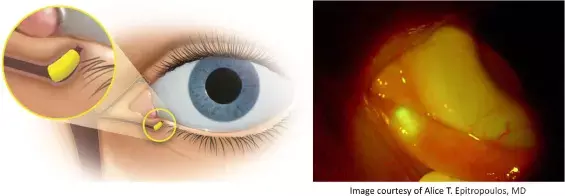
Courtesy by Eugene B. McLaurin et al., American Journal of Ophthalmology
Allergic conjunctivitis is reported in up to 40% of the general population and it is associated with a reduction in patients' quality of life. In a recent study, the researchers have found dexamethasone intracanalicular insert is well tolerated and provide relief of ocular itching for up to 4 weeks in patients with allergic conjunctivitis. The study findings were published in the American Journal of Ophthalmology on March 24, 2021.
Topical antihistamines, which competitively and reversibly block histamine receptors, are commonly used to treat allergic conjunctivitis and have a rapid onset but short duration of action, which requires multiple installations throughout the day. Corticosteroids can treat this response but, serious side effects are a concern. Because of safety issues due to side effects, both steroid-induced and preservative-induced, with long-term use, there is a continued unmet need for long-acting therapy with consistent efficacy, a reduced dosing burden, and an improved ability to inhibit the late-phase inflammatory response without inducing any serious side effects. Therefore, scientists developed intracanalicular dexamethasone insert to replace traditional corticosteroids drops. In this study, Dr Eugene B. McLaurin and his team conducted a phase 3 study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a dexamethasone intracanalicular ocular insert for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
It was a multicenter, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 clinical trial. The researchers randomly assigned the patients to dexamethasone insert or placebo insert to both eyes and evaluated using a modified version of the Ora-CAC® (conjunctival allergen challenge) model. After in-office insert placement, they conducted a series of 4 closely spaced post-insertion CACs at Weeks 1, 2, and 4 across approximately 30 days. The major outcomes assessed at Week 1 CAC Day 8 were subject-reported ocular itching at 3, 5, and 7 minutes post-CAC and researchers evaluated conjunctival redness at 7, 15, and 20 minutes post-CAC.
Key findings of the study were:
- Upon analysis, the researchers found that dexamethasone insert significantly lower mean ocular itch scores compared with placebo at all time points, with differences favouring dexamethasone insert over placebo (0.86, 0.98, and 0.96 units at 3, 5, and 7 minutes, respectively).
- However, they noted statistically significantly lower conjunctival redness scores at 20 minutes but not at 7 or 15 minutes.
- Upon further analysis, they found statistically significantly less itching and conjunctival redness at 31 and 29 of 33 other time points.
- They reported no adverse events and observed that one subject had elevated intraocular pressure in both eyes.
The authors concluded, "The data presented in this study demonstrate the potential for a single, physician-administered dexamethasone intracanalicular insert to provide relief of ocular itching for up to 4 weeks in subjects with allergic conjunctivitis, while maintaining a favorable safety profile."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


