- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
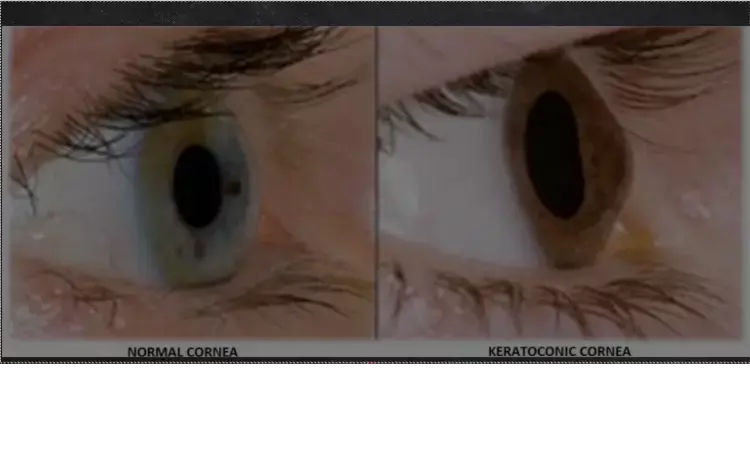
Low blood Riboflavin levels possible risk factor for keratoconus
Turkey: A new study found that low blood levels of riboflavin in Keratoconus patients could be one of the possible risk factors for the pathogenesis of Keratoconus. The study results were published in the Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery.
Keratoconus is a bilateral, inflammatory, and asymmetric disease that caused progressive thinning and steeping of the cornea ultimately leading to irregular astigmatism and decreased visual acuity. Literature shows that Riboflavin therapy has slowed the progression of Keratoconus thus increasing the corneal crosslinking. Hence researchers conducted a study to evaluate the effect of blood levels of vitamin B12, folic acid (B9), riboflavin (B2), and homocysteine in keratoconus (KC) and healthy subjects.
A prospective, cross-sectional study was carried out in the Eskişehir Osmangazi University (ESOGÜ) Hospital Eye Clinic between October 2019 and March 2020. Nearly 100 KC patients (patient group) between the ages of 18–35 years and 200 healthy individuals (control group) in the same age range were included. A complete ophthalmologic examination was done for all the participants and corneal tomography evaluation with a Pentacam Scheimpflug camera was performed. Using an electrochemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer blood levels of vitamin B12 and folic acid levels were measured, and high-performance liquid chromatography was used to assess the homocysteine and riboflavin levels. Categorical variables were analyzed using Chi-square tests and Mann–Whitney U and Kruskal–Wallis tests were used in the analysis of numerical variables.
Key findings:
- Homocysteine (p=0.190), vitamin B12 (p=0.619), and folic acid (p=0.230) levels were not different between KC and control groups.
| Levels | KC | Control |
| Homocysteine | 13.0±6.6 µmol/L | 12.1±5.4 µmol/L |
vitamin B12 | 313.5±119.4 pg/mL | 322.9±128.3 pg/mL |
folic acid | 7.0±2.7 ng/mL | 7.4±2.9 ng/mL |
mean riboflavin level | 84.0 ± 21.8 µg/L | 183.6±74.3 µg/L |
- The mean riboflavin level was less in the patient group when compared to the control group, with a significant difference between the two groups (p<0.001).
- Riboflavin levels were below 180 µg/L in 99% (n=99) of the cases in the KC group and 53.5% (n=107) in the control group (p<0.001).
Thus, low blood riboflavin levels could be one of the possible risk factors in the pathogenesis of Keratoconus.
Further reading: Sozer O, Ozalp O, Atalay E, Demir SS, Alatas İO, Yildirim N. Comparison of Blood Levels of Vitamin B12, Folic Acid (B9), Riboflavin (B2), and Homocysteine in Keratoconus and Healthy Subjects [published online ahead of print, 2023 Feb 2]. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2023;10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000001160. doi: 10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000001160
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751