- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Baricitinib Effective in Treating Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Lancet
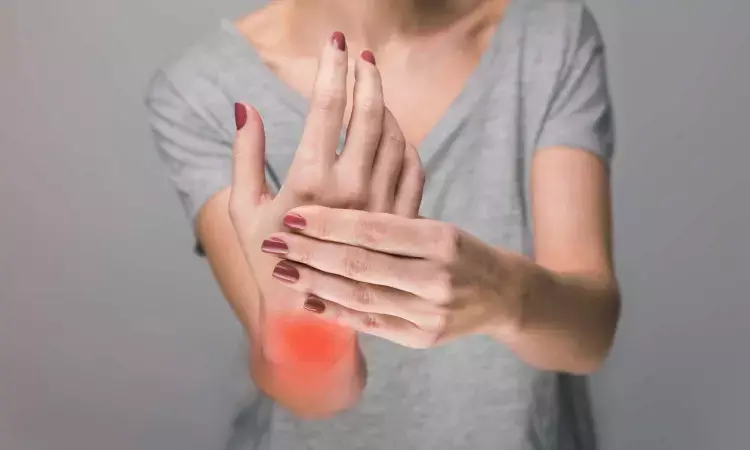
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a challenging condition to treat, especially in cases where traditional therapies fail to provide relief. However, a recent study published in The Lancet found the efficacy and safety of Baricitinib, an oral Janus kinase 1/2-selective inhibitor to fulfill as a potential treatment option for JIA.
This multinational study was conducted in 75 centers across 20 countries and enrolled patients aged 2 to under 18 years with various forms of JIA. These included polyarticular JIA, extended oligoarticular JIA, enthesitis-related arthritis, or juvenile psoriatic arthritis. All participants had shown an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more conventional synthetic or biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
The trial consisted of three periods: a 2-week safety and pharmacokinetic phase, a 12-week open-label lead-in period, and a placebo-controlled double-blind withdrawal period lasting up to 32 weeks. Patients received Baricitinib during the open-label lead-in phase, with dosages determined based on age.
Between December 2018 and March 2021, 220 patients participated in the study. Among them, 163 (74%) exhibited a positive response to Baricitinib during the open-label lead-in period and were randomly assigned to either placebo (81 patients) or continued Baricitinib treatment (82 patients) in the double-blind withdrawal period.
The primary endpoint of the trial was the time to disease flare during the double-blind withdrawal period. The results were remarkable, with the placebo group experiencing significantly shorter times to disease flare compared to the Baricitinib group, demonstrating the drug's efficacy in preventing disease relapse (hazard ratio 0.241, p<0.0001).
The safety profile of Baricitinib was also assessed, with few serious adverse events reported during the safety and pharmacokinetic phase or the open-label lead-in period. In the double-blind withdrawal period, serious adverse events occurred in four (5%) of 82 patients in the Baricitinib group and three (4%) of 81 patients in the placebo group. Notably, treatment-emergent infections were more frequent in the Baricitinib group (38%) compared to the placebo group (19%) during this period. These findings suggest that Baricitinib can be an effective and safe treatment option for JIA patients who do not respond well to standard therapies.
Source:
Ramanan, A. V., Quartier, P., Okamoto, N., Foeldvari, I., Spindler, A., Fingerhutová, Š., Antón, J., Wang, Z., Liao, R., Keller, S., Huemer, C., … Almeida, B. (2023). Baricitinib in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: an international, phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, withdrawal, efficacy, and safety trial. In The Lancet (Vol. 402, Issue 10401, pp. 555–570). Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00921-2
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


