- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
A Guide to Handle Artifacts of Dual-Energy CT
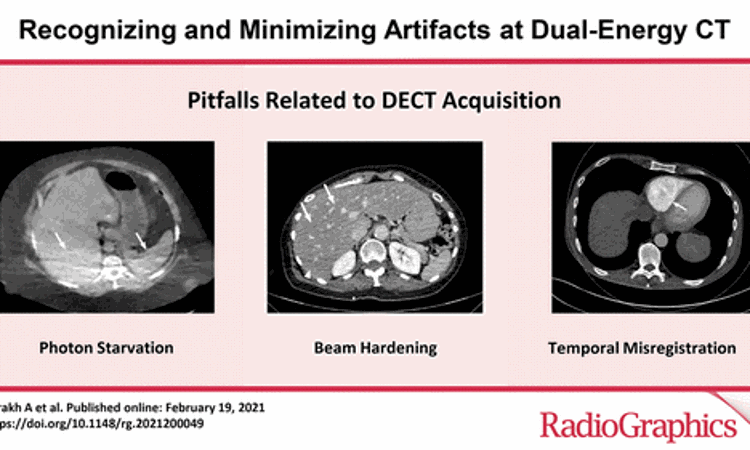
Dual-energy CT (DECT) is an exciting innovation in CT technology with profound capabilities to improve diagnosis and add value to patient care. A recent review article has recommended the radiologists and technologists to be aware of technological principles that may cause artifacts at dual-energy CT so that they can apply strategies to mitigate their occurrence and avoid diagnostic misinterpretation. The review report was published in the journal RadioGraphics on February 19, 2021.
DECT is a tremendous innovation in CT technology that allows the creation of numerous imaging datasets by enabling discrete acquisitions at more than one energy level. Technological advances and the proliferation of various processing methods have led to the availability of diverse vendor-based DECT approaches, each with a different acquisition and image reconstruction process.
The authors wrote in the report, "To enable effective use of DECT, one must be aware of the pitfalls and artifacts related to this technology." They further added, "The ability of radiologists and technologists to anticipate their (artifacts)occurrence and provide recommendations for proper selection of patients, intravenous and oral contrast media, and scan acquisition parameters are key to obtaining good-quality DECT images."
The team addressed radiologists to consider the following considerations when performing the DECT exams:
- Patient selection. Optimize DECT protocols by taking patient body weight and transverse diameter into consideration. "In patients with large body habitus, DECT may yield higher image noise and reduced image quality due to photon starvation," the team noted.
- Contrast medium selection. The appearance of iodine contrast appearance can be amplified on DECT, appearing as streaks on the image; reducing the iodine concentration in the contrast medium may be needed.
- Patient positioning. "Patients may need to be purposely off-centred to ensure that the organ of interest lies completely within the spectral field of view," the group cautioned.
- Temporal misregistration. This can affect image quality and lead to "spectral skew," in which data from the two energies being used are offset from each other.
- Image processing. Carefully select kernel, decomposition ratio, and thresholding parameters, the team wrote.
- Image display. Wider window settings are often needed to view DECT images.
The commentator wrote, "This article serves our community well in providing a high-level view of common DECT-related artifacts and makes a strong case that vendor-specific mitigation approaches must be considered."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


