- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
MRI myelography, a feasible alternative to CT for detecting CSF leaks: Study
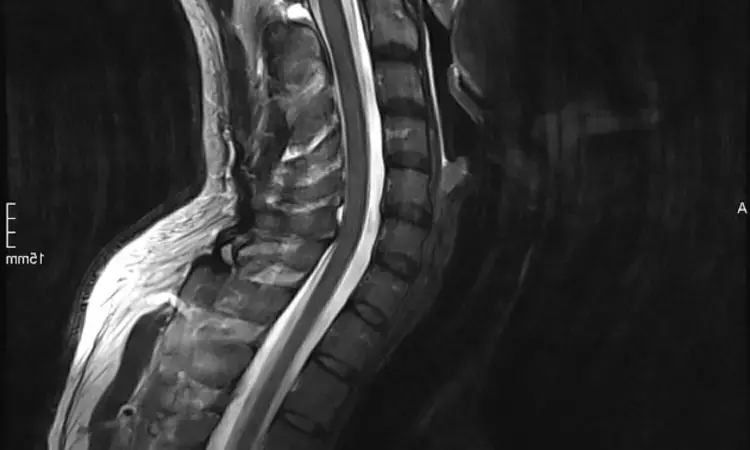
USA: MRI myelography is a less invasive way for detection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks in spontaneous intracranial hypotension patients compared to the CT version of the same exam, finds a recent study. Also, MRI myelography performed comparably to the CT version. The study is published as a research letter in JAMA Neurology.
According to a team of researchers led by Angelique Sao-Mai Sy Tay, Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues, the results could help clinicians expand their toolkit for patients suffering from this condition.
The authors wrote that "Eliminating radiation exposure, obviating the need for lumbar puncture and intrathecal contrast injection, and decreasing resource utilization and cost are among the most important advantages of MRM [MRI myelography] over CTM [CT myelography]."
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is an important cause of headaches. For initial evaluation of patients with suspected SIH, post-myelography computed tomography (CT myelography or CTM) has long been considered the gold standard for the detection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, but spine magnetic resonance imaging including heavily T2-weighted magnetic resonance myelography (MRM) may be a noninvasive alternative.
The researchers aimed to compare the diagnostic accuracy of MRM with CTM for the identification of spinal CSF leaks.
The study included 576 patients who underwent MR myelography and CT myelography exams. Of these, 276 (47.9%) were diagnosed with CSF leaks on both CT and MR myelography.
The results indicate MRI myelography could be a feasible alternative to CT.
The researchers found the following:
- MR myelography and CT myelography findings conflicted in less than 2% of patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension.
- Positive agreement between the two exams was 99.6%, negative agreement was 97.7%, and overall agreement 98.6%.
"MRM may be a suitable alternative to CTM for the initial evaluation of patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension," the authors concluded.
Reference:
The study titled, "Computed Tomography vs Heavily T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Myelography for the Initial Evaluation of Patients With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension," is published in JAMA Neurology.
DOI:https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/article-abstract/2783666
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


