- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rare case of congenital Morgagni hernia presenting with chest pain - a report
Dr Mujtaba Mohamed at Department of Medicine, Hackensack Meridian Health Jersey Shore University Medical Center, Neptune, USA has reported a rare case of congenital Morgagni hernia presenting as chest pain. The case has been published in the journal of Medical case reports.
Morgagni hernia is a rare form of congenital diaphragmatic hernia with a prevalence of 2–3%. It occurs due to a defect on the anterior part of the diaphragm, which allows abdominal organs to penetrate into the thoracic cavity. This condition can be detected during fetal life by routine ultrasonography or late during adult life. Late diagnosis of this condition in adults is extremely rare. The authors have reported a case of a patient who presented with chest pain due to newly diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
According to history, a 29-year-old unemployed white man with no significant past medical history presented to the hospital with a 1-month history of intermittent chest pain.
He was a current smoker with a one-pack-per-day habit and a family history of coronary artery disease on his father's side. He presented to the emergency room of our hospital with a 1-month history of intermittent chest pain. His chest pain was localized to the right side and was pressure-like, of moderate-intensity 4–6/10, nonradiating, and relieved by standing up and worsened by lying flat, but otherwise, it was not changed with an increase or decrease in activity level. He had no associated palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or lower extremity edema. He had been taking ibuprofen 500 mg orally as needed at home in an attempt to relieve his pain. Two days prior to this presentation, his chest pain became more constant with the same quality. On the day of admission, he developed difficulty in swallowing food. He experienced dysphagia (food stuck in the lower part of his esophagus); however, he had no associated nausea or vomiting.
His physical examination revealed the following vital signs: blood pressure 144/75 mmHg and heart rate 72 beats per minute. Pulse oximetry showed his oxygenation was 99% on room air. Examination of his head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat revealed that his condition was normocephalic and atraumatic. His extraocular movements were intact. His pharynx was clear. His neck was supple without jugular vein distention. His chest wall was nontender. His lungs had clear breath sounds bilaterally without any evidence of wheezing, rales, or rhonchi. His cardiac examination revealed a regular rate and rhythm. His abdomen was soft and nontender with positive bowel sounds. His neurological examination revealed that he was alert and oriented to time, place, and person. His sensation was intact; he had no facial droop, and his pupils were equal and reactive to light and accommodation. His cranial nerves were intact. His power was 5/5 in all four extremities. His reflexes were intact. His complete blood count findings were as follows: white blood cell count 8300/μl (normal range 4500–11,000/μl), hemoglobin 14.4 mg/dl (12–16 mg/dl), hematocrit 41% (35–48%; 12–17.5 g/dl), and platelet count 273,000 (140,000–450,000/μl). His blood chemistry findings were as follows: sodium 139 mmol/ (normal range 135–145 mmol/L), potassium 4.1 mmol/dl (3.5–5.2 mmol/dl), chloride 106 mmol/L (96–110 mmol/L), CO2 27 mmol/L (24–31 mmol/L), glucose 105 mg/dl (70–99 mg/dl), blood urea nitrogen 7 mg/dl (5–25 mg/dl), creatinine 0.72 mg/dl (0.44–1.0 mg/dl), aspartate aminotransferase 16 IU/L (10–42 IU/L), alanine aminotransferase 21 IU/L (10–60 IU/L), calcium 9.6 mg/dl (8.5–10.5 mg/dl), bilirubin 0.5 mg/dl (0.2–1.3 mg/dl), and lactate 1.0 mmol/dl (0.5–2.0 mmol/dl). His international normalized ratio was 1.14 (normal range 2–3 with conventional anticoagulation).
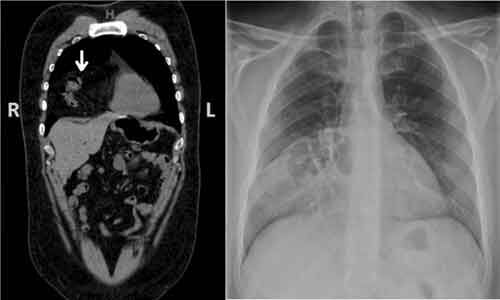
The finding of his electrocardiogram (ECG) was negative for any ST changes. The patient's chest x-ray showed a suspected loop of bowel on the right side of the chest (Fig. 1). Subsequently, the patient underwent CT of the chest, which showed a 7-cm defect in the right hemidiaphragm anteriorly with a large amount of intra-abdominal fat and a loop of proximal transverse colon within the hernial sac (diaphragmatic hernia of Morgagni). The herniated contents were located in the right pericardial location (Figs. 2, 3, and 4). A nasogastric tube was inserted to decompress the bowel. The patient was evaluated by a surgeon. Eventually, the patient underwent laparoscopic repair of his diaphragmatic hernia (Figs. 5, 6, and 7) with a successful outcome. His chest pain and dysphagia resolved completely. When he was seen 6 months later for a follow-up, he was completely asymptomatic without any complications.
For more details click on the link: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-2336-9
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


