- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Palpae Potami: The new proposed method for locating the dorsalis pedis artery
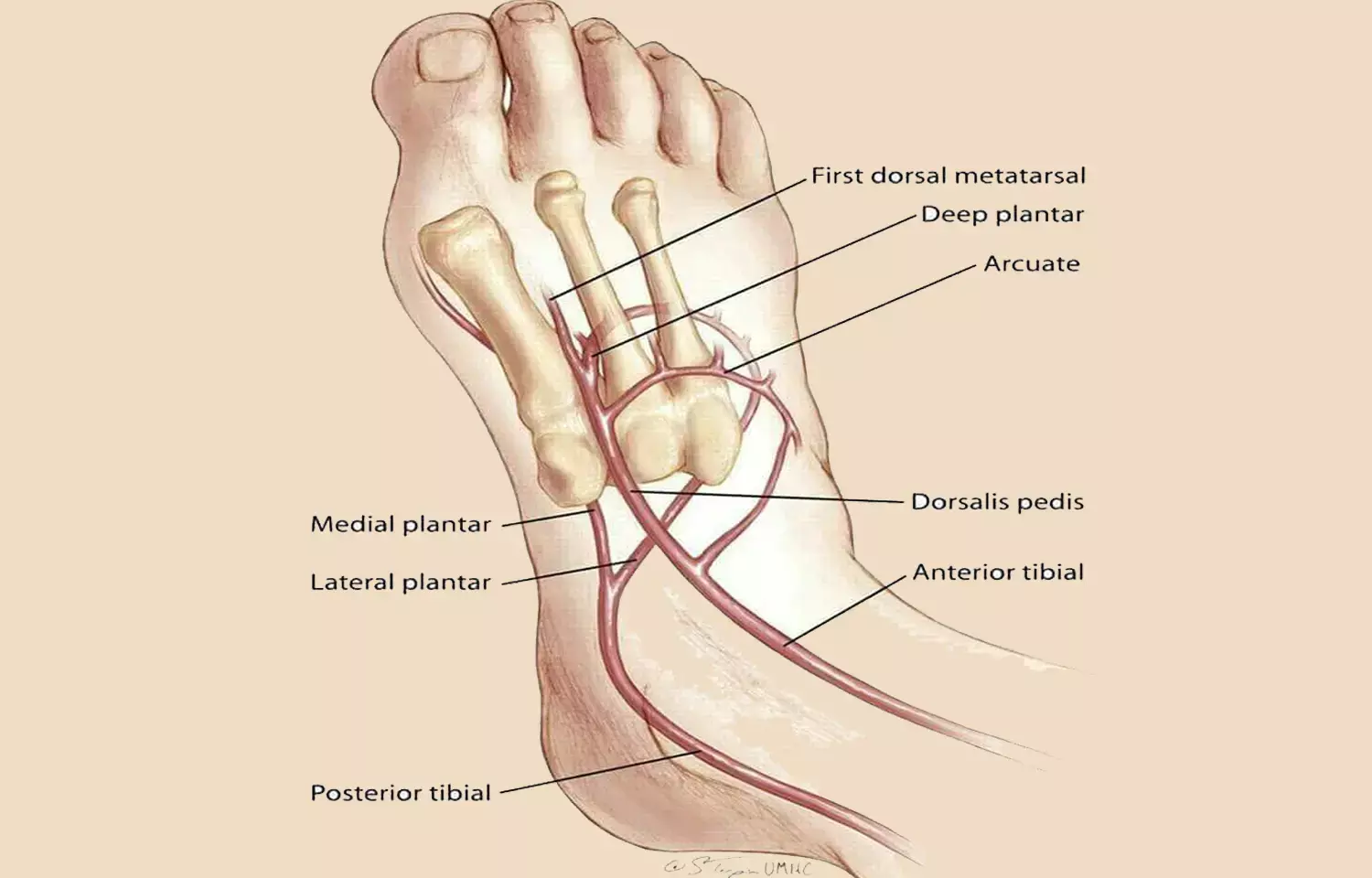
According to a recent study, researchers have found a new method that increases the chance of palpating the dorsalis pedis artery significantly higher than by the conventional method.
The research is published in the Indian Journal of Surgery.
The peripheral pulse examination of the foot is the preliminary yet important step in diagnosing peripheral vascular diseases. It has been reported that locating the dorsalis pedis pulse is difficult with existing variability among examiners when compared with another distal foot pulse examination. Ill-defined landmarks and a high rate of aberrant course of the artery have been attributed for its difficulty hence its palpation becomes a challenging task.
Therefore, Aravind Ravichandran and Aparnaa Balasubramanian from the Government Theni Medical College, Madurai, India formulated a new method for examination of dorsalis pedis pulse.
The authors studied a total of 102 patients who were admitted in a tertiary care center where their dorsalis pedis pulse was examined by portable Doppler and clinical methods. Two examiners, double-blinded examined the dorsalis pedis artery using the conventional method and the new method independently, and documented their findings.
The key findings highlighted from the study were-
a. Dorsalis pedis pulse was impalpable in 2.9% of cases by both methods.
b. The palpae potami method located the dorsalis pedis pulse in 90% of cases, while the conventional method located dorsalis pedis pulse in 83.3% of cases.
c. The palpae potami method has better sensitivity and specificity of 96.8% and 75%, respectively, while the conventional method had sensitivity and specificity of 86% and 50%, respectively.
d. The mean duration taken by a conventional method to locate the pulse was 4.7 s, while palpae potami took 31 s.
e. The absence of dorsalis pulse was seen in 7.2% of the cases.
f. The presence of systemic hypertension in patients lower the dorsalis pedis pulse detection in the conventional method (p = 0.0023), while no significant difference in pulse detection was found by the palpae potami method.
Therefore, the authors concluded that "the new method devised method increased the chance of locating the dorsalis pedis artery significantly than by conventional method which could be translated to higher case pickup of peripheral vascular diseases in a resource-limited setting."
The difficulties encountered by the conventional method in locating dorsalis pedis pulse could be reduced by this method, they further added.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


