- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pyeloplasty safe, effective in kidneys with poor function also: Study
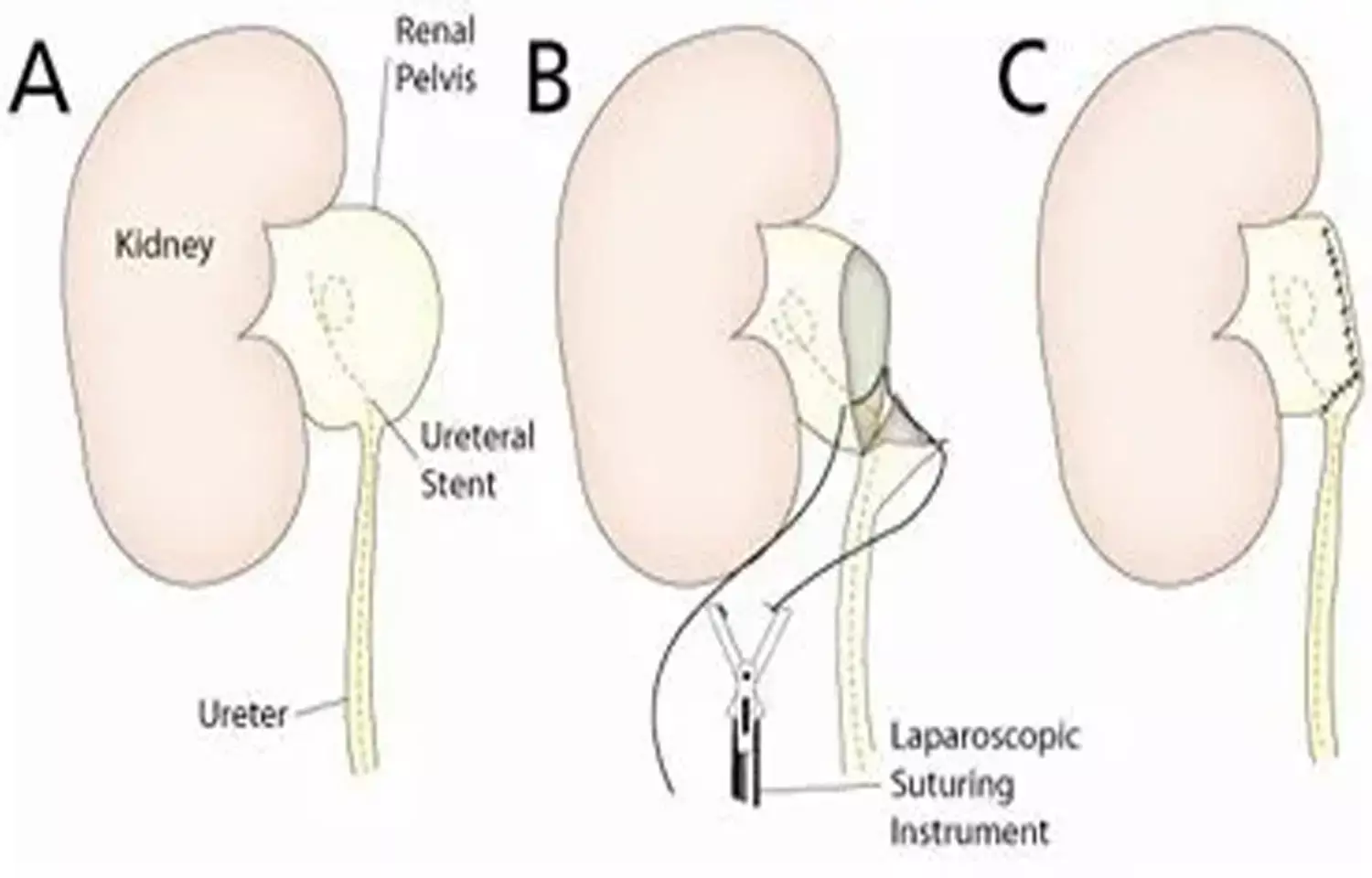
USA: Pyeloplasty is equally safe and effective in poorly functional kidney and in kidney with better renal function, finds a recent study in the Journal of Pediatric Urology. According to the study, preoperative differential renal function did not predict success rate of pyeloplasty. Patients having DRF ≤10% did not have higher incidence of complications or failure rate.
In short, DRF alone should not effect the management options available for ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) patients, wrote the authors.
Indications for UPJO treatment include urinary tract infections, symptomatic obstruction, worsening differential renal function (DRF) and/or presence of an obstructive pattern on functional renal scan. Arun K. Srinivasan, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA, and colleagues hypothesized that low preoperative DRF is not an independent predictor of pyeloplasty failure.
To test the hypothesis, the researchers performed a retrospective chart review for identifying all patients undergoing pyeloplasty for UPJO between 2008 and 2019. It included 364 patients who met inclusion criteria of having at least one preoperative functional scan and a minimum of one renal ultrasound post-operatively.
Patients were divided into three groups based on DRF for analysis: Group 1- 0-10% (n=1), Group 2 - >10-≤20% (n=24), Group 3 - >20% (n=332). The researchers then compared Baseline, intraoperative and postoperative characteristics, including success and complications.
Key findings of the study include:
- Mean procedure time was longest for the ≤10% function group (237.9 vs 206.4 vs 189.1).
- There was no difference in 30-day post-operative complications, overall success rate or the need for additional procedures among the three groups.
- For patients in Group 1, we noted variation in the post-procedure DRF with a range of −2.8 to +47% change.
- In this group, none of patients with low DRF underwent nephrectomy.
- Multivariate logistic regression did not identify renal function as a predictor of operative success OR 1.00.
"The results of the present study suggest that low DRF alone is not associated with worse outcomes and shows no difference in the failure rate. The incidence and type of complications were not increased for the lower functioning groups," wrote the authors.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


