- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Diabetes tied to increased penetration of rotary instruments into dentin in root canal procedures
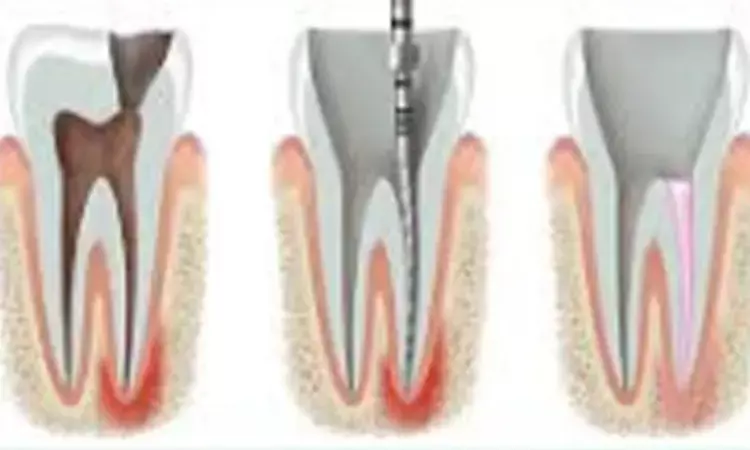
Diabetes mellitus (DM) may affect the physical and mechanical properties of dentin, which could potentially have an impact on root canal procedures. The dentin of patients suffering from both diabetic type 1 (D1), diabetic type 2 (D2) exhibited an increased amount of dentin removed compared with the nondiabetic dentin specimens, reported a recent study published in the Journal of Endodontics.
The team of researchers led by Mohammad Ali Saghiri at the Biomaterial and Prosthodontic Laboratory, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Rutgers School of Dental Medicine, Newark, New Jersey aimed to compare the amount of dentin removed by an endodontic rotary file, comparing dentin from diabetic patients with dentin from control patients under laboratory conditions.
The amount of dentin removed was tested using new F3 ProTaper (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) files applied against the surface of prepared dentin discs for 3 different groups-
a. diabetic type 1 (D1),
b. diabetic type 2 (D2), and
c. nondiabetic (normal).
The dentin removed was determined by measuring the depth of penetration of the file using a digital caliper and by measuring the weight loss.
Data were analyzed using Kolmogorov-Smirnov, analysis of variance, post hoc Tukey, and Pearson correlation tests (P < .05).
The following findings were highlighted-
a. Significantly more dentin was removed, and the penetration of the F3 instrument was significantly higher (P < .05) in diabetes mellitus specimens.
b. The statistical analysis revealed significant differences between the type 1 and type 2 diabetes and normal groups (P < .05) for the weight loss of the specimen as well as the penetration depth at point B (P < .05).
c. Both the weight loss and depth of penetration showed a very high positive correlation (P < .05).
As a result, the authors concluded that the dentin of patients suffering from both D1 and D2 exhibited an increased amount of dentin removed compared with the nondiabetic dentin specimens.
This can be observed by the increased penetration of the rotary instruments into dentin. Under certain circumstances, this may impact instrumentation, increasing procedural accidents and leading to subsequent weakening of root canal–treated teeth in diabetic patients.
For further reading, log in to:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2021.03.019
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


