- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Glass Ionomer Cement Fissure Sealants useful as non-aerosol-generating procedure in paediatric patients
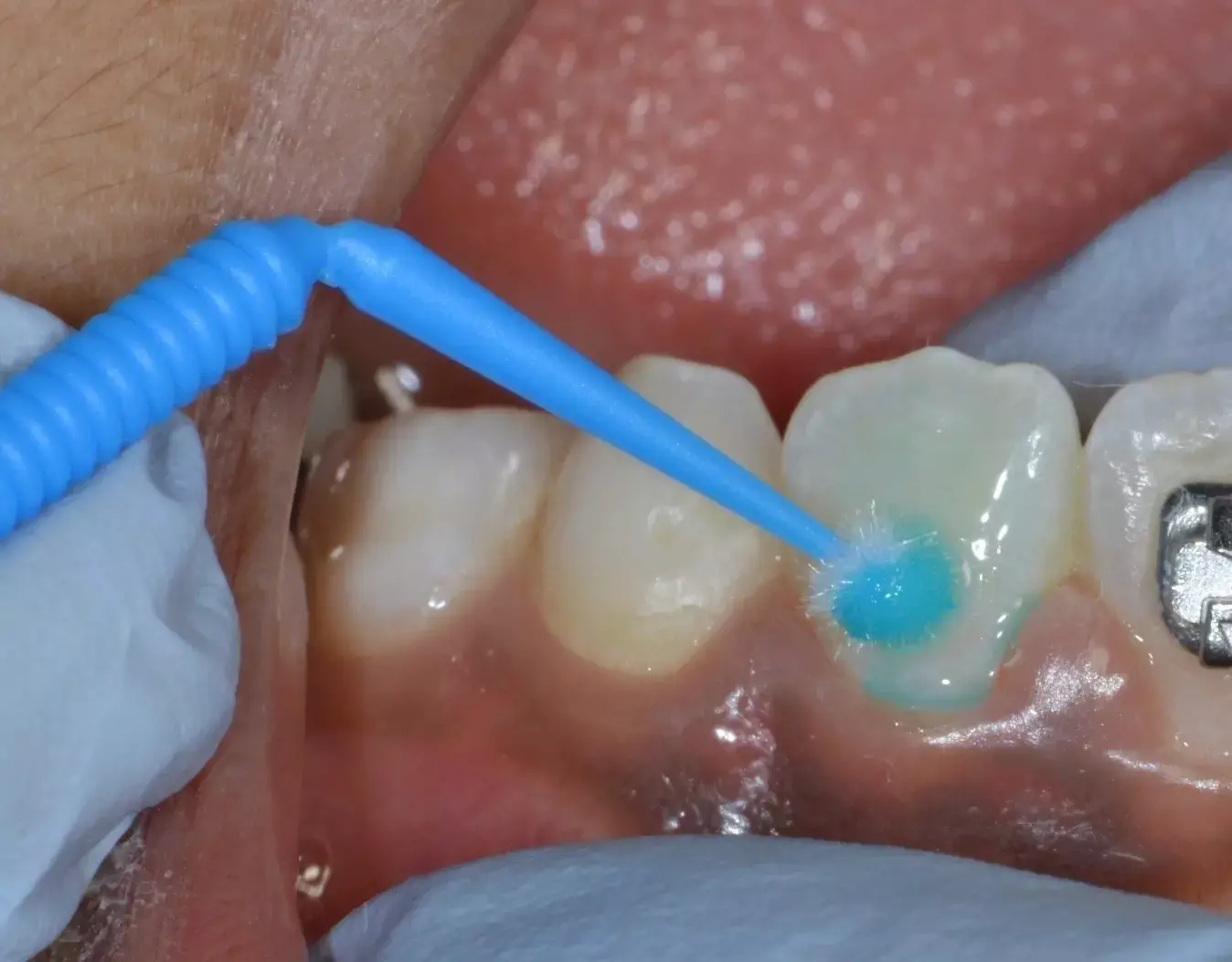
Researchers have found in a new study that Glass Ionomer Cement Fissure Sealants are useful as non-aerosol-generating procedure in paediatric patients. They are beneficial as preventative fissure sealant for first permanent molars in high caries risk patients waiting general anaesthetic.Therefore ongoing use of Glass Ionomer Cement Fissure Sealants where close patient monitoring is available is beneficial.
The study was published in the British Dental Journal Open.
The aim of this case series was to assess the ongoing suitability of Glass Ionomer Cement Fissure Sealants for use in paediatric patients. These had been used through the COVID pandemic due to their status as a non-aerosol-generating procedure.
A retrospective clinical review was undertaken to identify cases where GIC Fissure Sealants were used in paediatric patients awaiting exodontia general anaesthetic within Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Community Dental Service. Identified cases were then collated to form this case series. These were reviewed regarding the number of GIC fissure sealants placed, and retention at the GA appointment and any subsequent follow-up appointments.
Results:
The results showed favourable results of Glass Ionomer Cement fissure sealants, with an average retention of 77% – in line with the wider literature results for Glass Ionomer Cement fissure sealants.
The results showed a favourable retention rate, particularly given patient challenges leading to them requiring exodontia general anaesthesia. Review of alternative fissure sealant materials may be beneficial on a local level to compare results with the available literature and confirm ongoing suitability.
Although the restrictions due to the pandemic have eased, this paper supports and adds to the existing evidence base on the efficacy of Glass Ionomer Cement Fissure Sealants applications if RB-FSs are not achievable within the local setting and context. It further suggests that the appropriateness of GIC-FS should be considered in cases where broader limitations, such as clinical demands, time constraints, or national restrictions to practice are present.
The results appear to support the ongoing use of Glass Ionomer Cement Fissure Sealants where close patient monitoring is available.
Reference:
Mummery, T.A., Popat, R. Glass Ionomer Cement as a preventative fissure sealant for first permanent molars in high caries risk patients waiting general anaesthetic—a case series. BDJ Open 8, 25 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41405-022-00119-3
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


