- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Serum biomarkers and CCTA may predict MACE among patients with acute chest pain with normal ECG
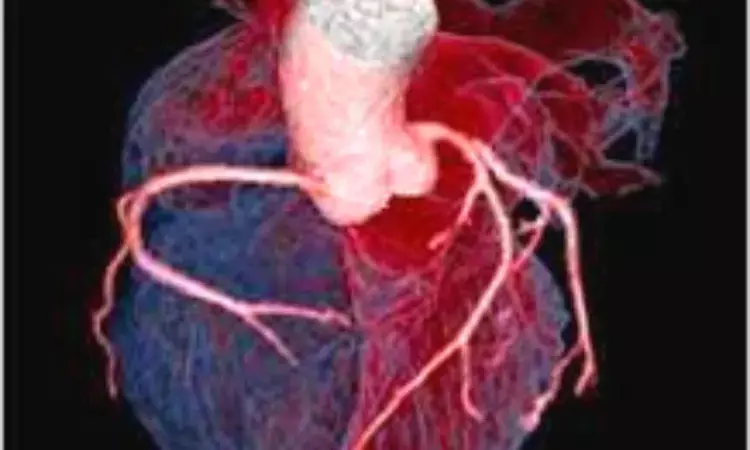
China: Serum amyloid A, apoB/apoA1, and the number of atherosclerotic vessels are the most powerful predictors of MACE among patients with acute chest pain and normal ECG at three-month and one-year follow-ups, a recent study has stated. The prospective cohort study appears in The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging.
The study was conducted by Gaofeng Zhang, Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi City, China, and colleagues with the objective to assess the prognostic value of coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) and serum biomarkers for the major adverse cardiac events (MACE) prediction at three-month and one-year follow-ups.
For this purpose, the researchers included a total of 720 patients with acute chest pain and normal electrocardiography (ECG). Followed by 3-month and 1-year follow-up for MACE occurrence, these patients received both coronary CTA screening and serum biomarkers testing. The occurrence of MACE, which is defined as an acute coronary syndrome (ACS), nonfatal MI, and all-cause mortality was the primary outcome.
The study led to the following findings:
- The MACE rate was 17.8% and 25.2% at three-month and one-year follow-ups.
- ApoB/apoA1(OR = 7.45) and the number of atherosclerotic vessels (OR = 2.86) were independent predictors for MACE at the three-month follow-up, so were apoB/apoA1 (OR = 5.23), Serum amyloid protein A (SAA, OR = 1.04) and the number of atherosclerotic vessels (OR = 2.54) at the one-year follow-up.
- While apoB/apoA1 suggested its sensitivities of 84% for predicting MACE at three-month follow-ups, the number of atherosclerotic vessels had 81% specificity at one-year follow-up.
"The findings suggest the integration of apoB/apoA1, SAA and number of atherosclerotic vessels into cardiovascular risk evaluation and individual prevention," the researchers conclude.
They wrote in their study, "At three-months and one-year follow-ups, apoB/apoA1, SAA and number of atherosclerotic vessels are the most powerful predictors of MACE among patients with acute chest pain and normal ECG."
Reference:
Huang, H., Ye, F., Huang, Y. et al. Coronary CT angiography and serum biomarkers are potential biomarkers for predicting MACE at three-months and one-year follow-up. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-022-02646-4
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


