- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Nerve decompression may reduce pain in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Study
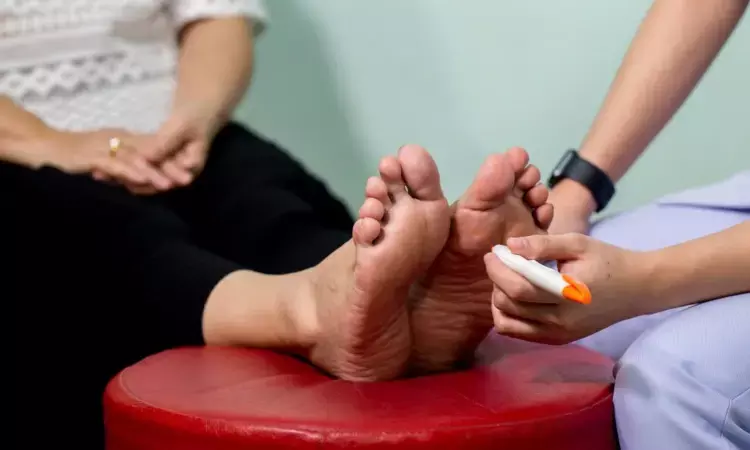
A recent study by the team led by Shai Rozen unveiled the effectiveness of nerve decompression surgery in patients requiring the treatment for painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN). This condition usually affects millions globally and often leads to significant discomfort and pain in the lower extremities which severely impacts the quality of life. The key highlights of this study were published in the newest edition of Annals of Surgery.
This rigorous double-blinded, randomized trial compared the outcomes of nerve decompression surgery against the observation and sham surgery. This study encompassed a broad age range of patients from 18 to 80 years and who had not found relief from one year of medical treatment. The research ensured a comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of surgery by randomizing patients to either undergo nerve decompression on one leg with a sham surgery on the other or to an observation group.
After 12 months, the patients who underwent nerve decompression reported a significant reduction in pain when compared to the control group. With mean differences in pain scores significantly lower in both the right and left decompression groups. Also, both decompressed and sham-operated legs showed equal improvement initially which suggests a complex interplay of physical and psychological factors in pain perception.
However, the long-term findings which was observed at 56 months showed that patients who had undergone nerve decompression maintained a lower level of pain when compared to controls where the difference in pain scores were both clinically and statistically significant. Also, a direct comparison between decompressed and sham-operated legs revealed a clear advantage for the former that indicated a true effect of the surgery beyond placebo.
These crucial findings in the individuals with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy suggests that nerve decompression surgery could become a cornerstone in the management of this challenging condition. The outcomes caution that the observed benefits necessitate further scrutiny despite being promising. Overall, the potential placebo effect highlighted by the initial improvement in sham-operated legs strongly underline the complexity of treating chronic pain conditions and the need for a deeper understanding of how surgical interventions exert their effects.
Reference:
Rozen, S. M., Wolfe, G. I., Vernino, S., Raskin, P., Hynan, L. S., Wyne, K., Fulmer, R., Pandian, G., Sharma, S. K., Mohanty, A. J., Sanchez, C. V., Hembd, A., & Gorman, A. (2024). Effect of Lower Extremity Nerve Decompression in Patients with Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. In Annals of Surgery. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000006228
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


