- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Another plus for Statins- May help treat xanthelasmas
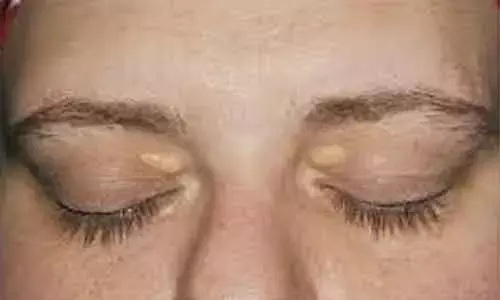
Xanthelasmas are asymptomatic, benign, yellowish papules or plaques that appear on or around the eyelids. They comprise of cholesterol-loaded macrophages and typically develop in adulthood. In about half of cases, they are associated with familial hypercholesterolemia; thus, they should trigger lipid profiling. In patients with familial hypercholesterolemia, regression of xanthelasmas can occur with lipid-lowering drugs, such as statins
Researchers from the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Western University, London, Ontario, Canada, observed the regression of xanthelasmas in a patient with normal lipid levels after treatment with a statin. Typical treatments for patients with xanthelasmas with normal lipid levels carry risks and high recurrence rates. The Case Report is published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Earlier studies have found role Alirocumab in early resolution of Xanthelasmas but the role of statins was not established.
Xanthelasmas are benign, yellowish growths made up of cholesterol under the skin that appear on or around the eyelids. In about half of cases, they are associated with familial high cholesterol. In these patients, regression of xanthelasmas can occur with lipid-lowering drugs, such as statins. Many patients with xanthelasmas, however, have normal lipid levels. In these patients, xanthelasmas can be removed with liquid nitrogen, topical trichloroacetic acid, laser ablation, or surgical excision, but these therapies all carry a risk for scarring or residual pigmentation and high recurrence rates (up to 40 per cent).
To report the effect of statin therapy for a person with xanthelasmas with normal lipid levels, researchers prescribed 10 mg of rosuvastatin, a statin to help lower "bad" cholesterol (mainly LDL) and raise "good" cholesterol, to a 52-year-old woman with normal lipid levels who wanted her xanthelasmas removed for cosmetic reasons. Within three months of treatment, the patient's LDL cholesterol level had decreased by 50 per cent, remaining steadily in that range for the next four years. Within 12 months, she reported some regression of her xanthelasmas, and after four years of rosuvastatin, they had almost completely regressed.
For further reference log on to:
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


