- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Microneedles may effectively deliver local anaesthesia in dental procedures: Study
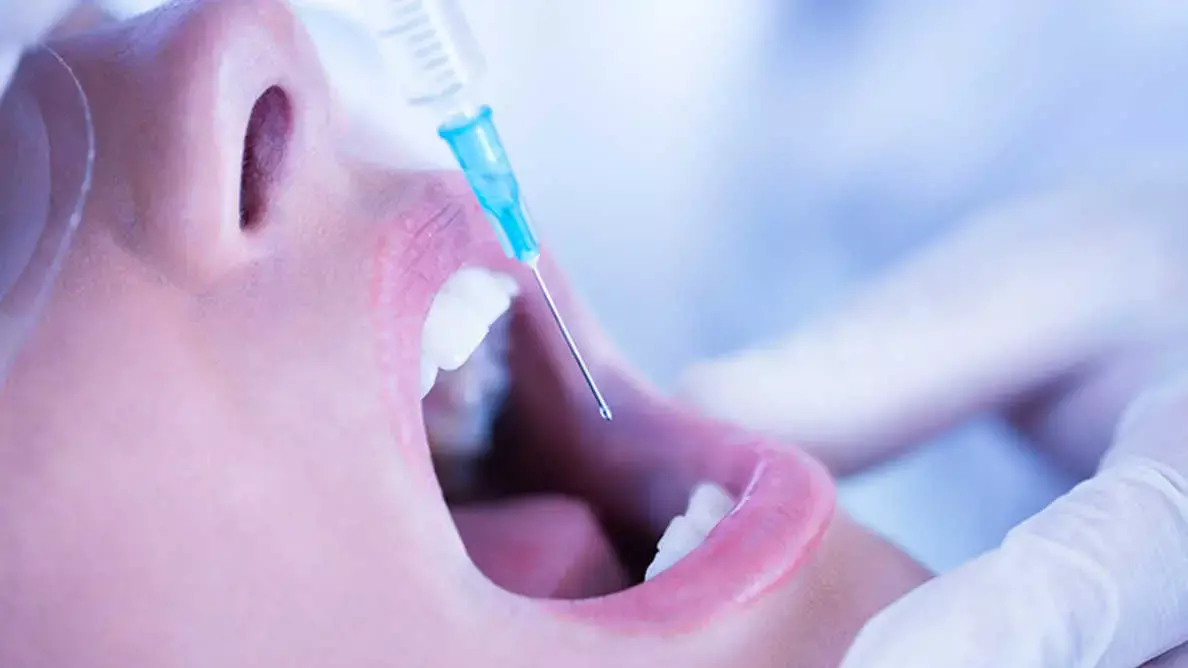
Microneedles (MNs) for local anaesthesia delivery are as successful as the current gold standard, according to a study published in the Advanced Functional Materials
Pain management during dental procedures is a cornerstone for successful daily practice. In current practice, the traditional needle and syringe injection are used to administer local anaesthesia. Perhaps the most common tool for dental pain management is a 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (HCl) solution with 1:100,000 epinephrine. A cartridge with up to 1.8 ml of 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine provides the duration of approximately 60 to 90 minutes when using an injection block technique for pulpal anaesthesia. Any cartridge may contain 1.8 ml of solution, but the average volume is 1.76 ml and recommendations to calculate dosage should err on the higher volume for safety purposes.
However, the appearance of long needles and the pain associated with it often leads to dental anxiety deterring timely interventions. Microneedles (MNs) has emerged as a minimally invasive alternative to hypodermic needles and shown to be effective in transdermal drug delivery applications.
A study was conducted by a team of researchers to examine the potential use of Microneedles (MNs) for local anaesthesia delivery in dentistry.
The researchers found that:
- The development of a novel conductive Microneedles (MNs) array that can be used in combination with iontophoresis technique to achieve drug penetration through the oral mucosa and the underlying bone tissue is presented.
- The conductive Microneedles (MNs) array plays a dual role, creating micro-conduits and lowering the resistance of the oral mucosa.
- The reduced tissue resistance further enhances the application of a low-voltage current that can direct and accelerate the drug molecules to target the sensory nerves supplying teeth.
Thus, the researchers concluded that the successful delivery of lidocaine using this new strategy in a clinically relevant rabbit incisor model is shown to be as effective as the current gold standard.
Reference:
A study titled, "Targeted Delivery of Anesthetic Agents to Bone Tissues using Conductive Microneedles Enhanced Iontophoresis for Painless Dental Anesthesia" by Razina Z. Seeni published in the Advanced Functional Materials
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202105686
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


